Distribution characteristics of carbon storage in forest ecosystems in typical watersheds of Taihang Mountains Basin
-
摘要:
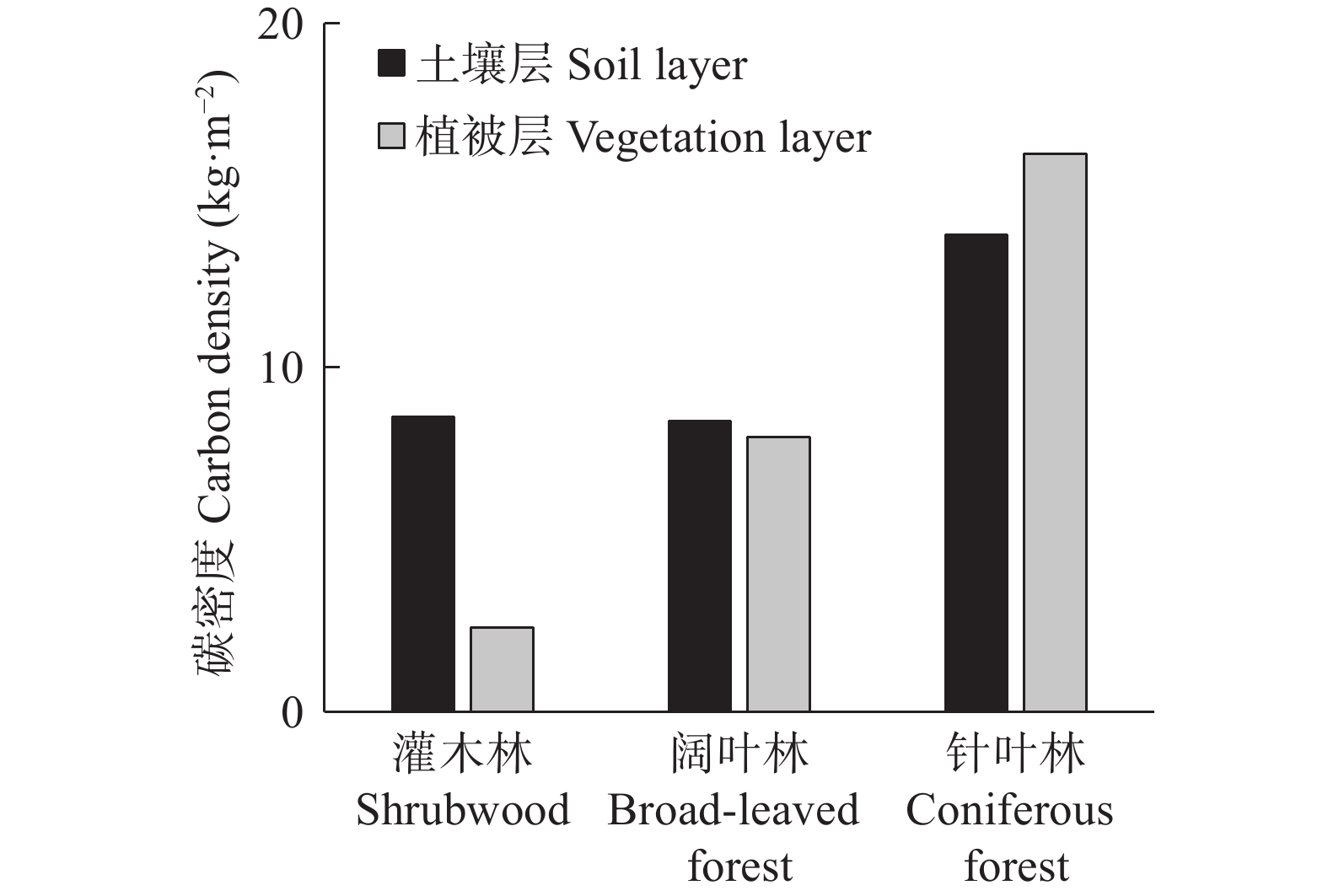
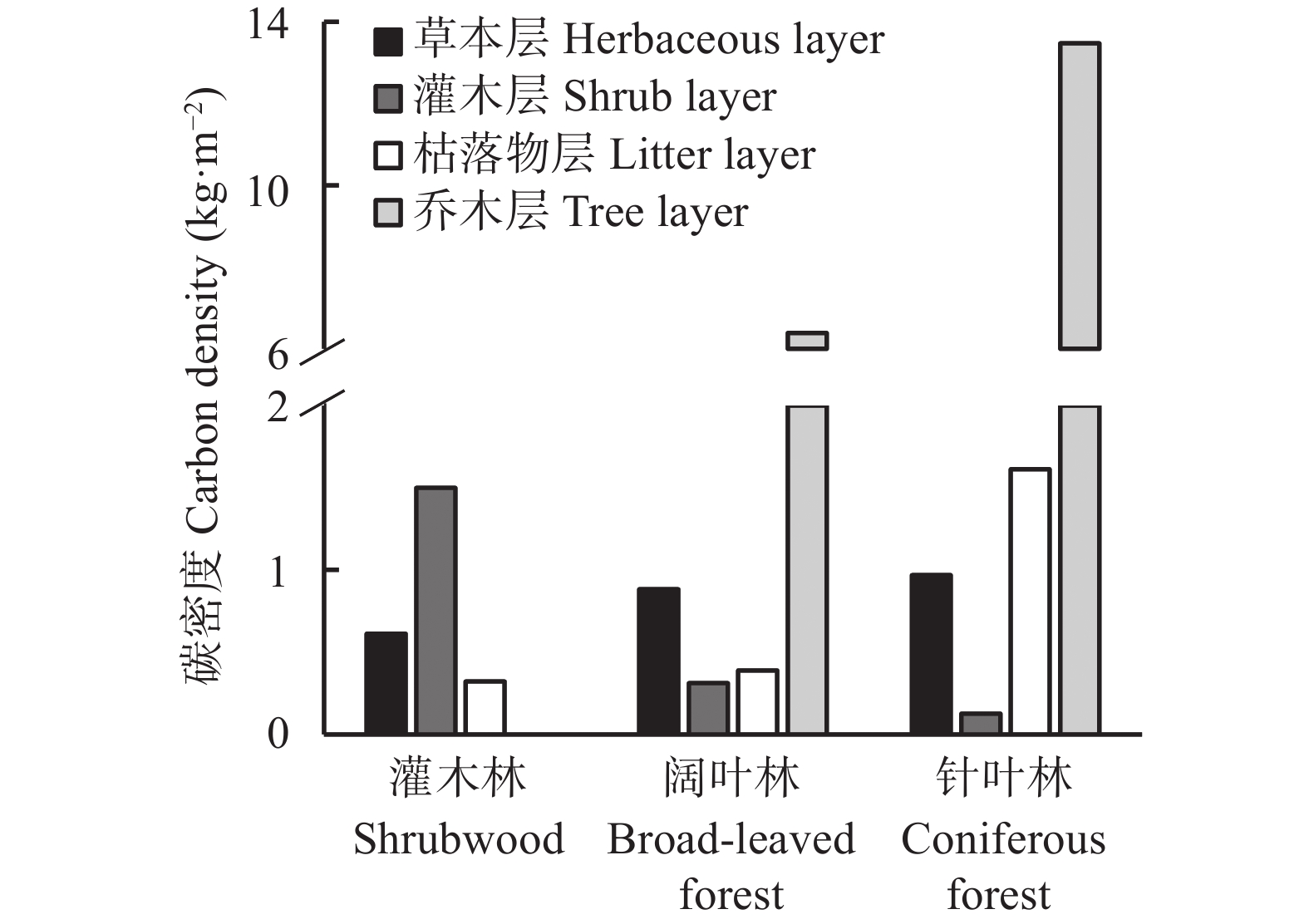
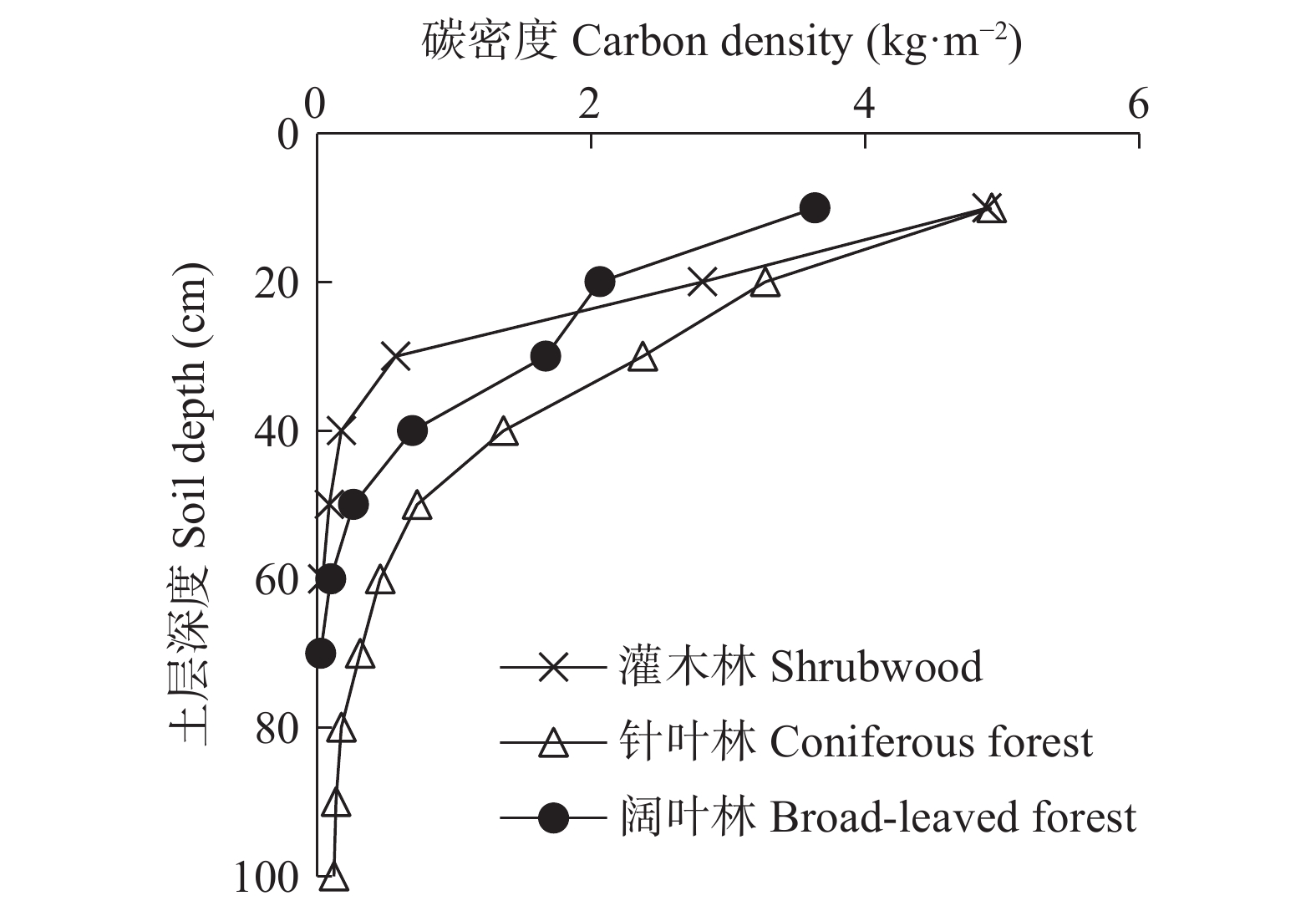
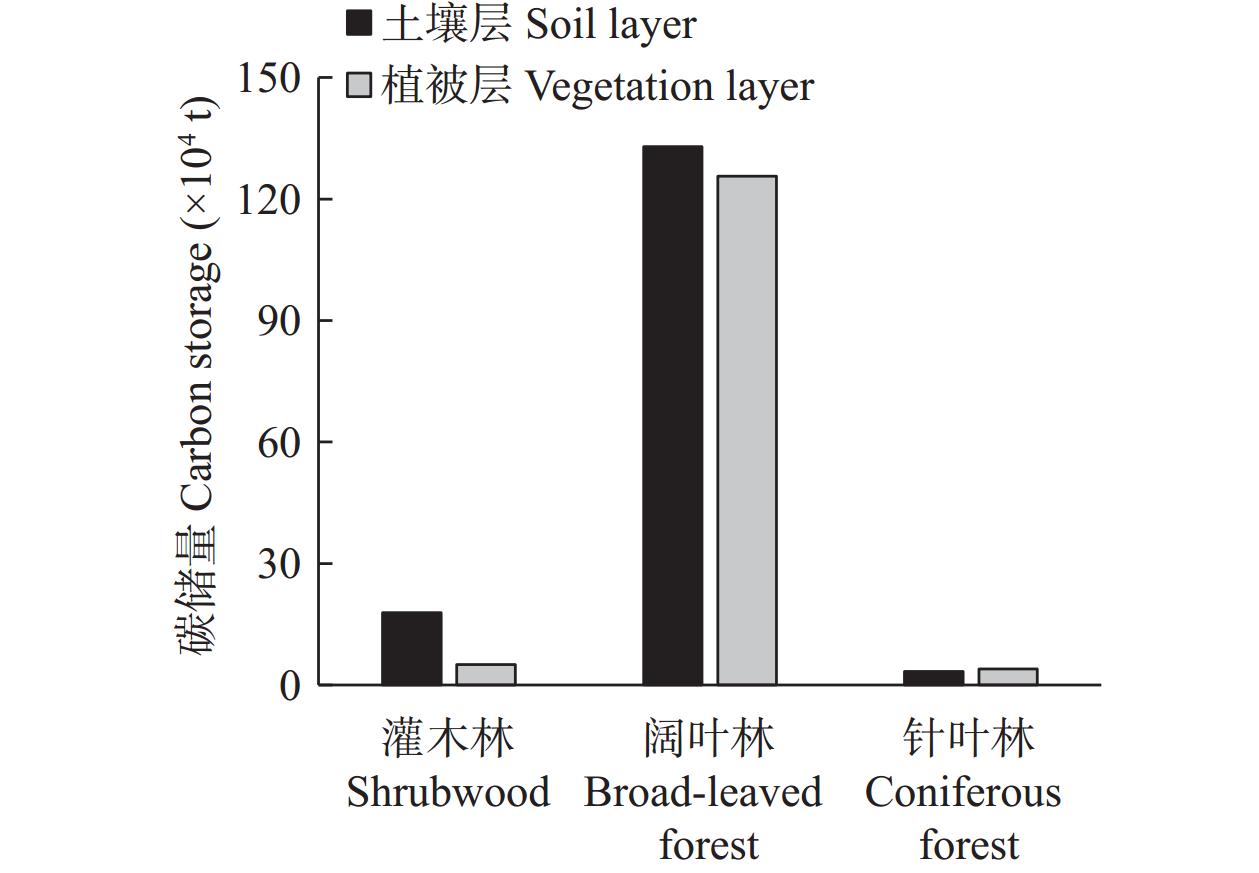
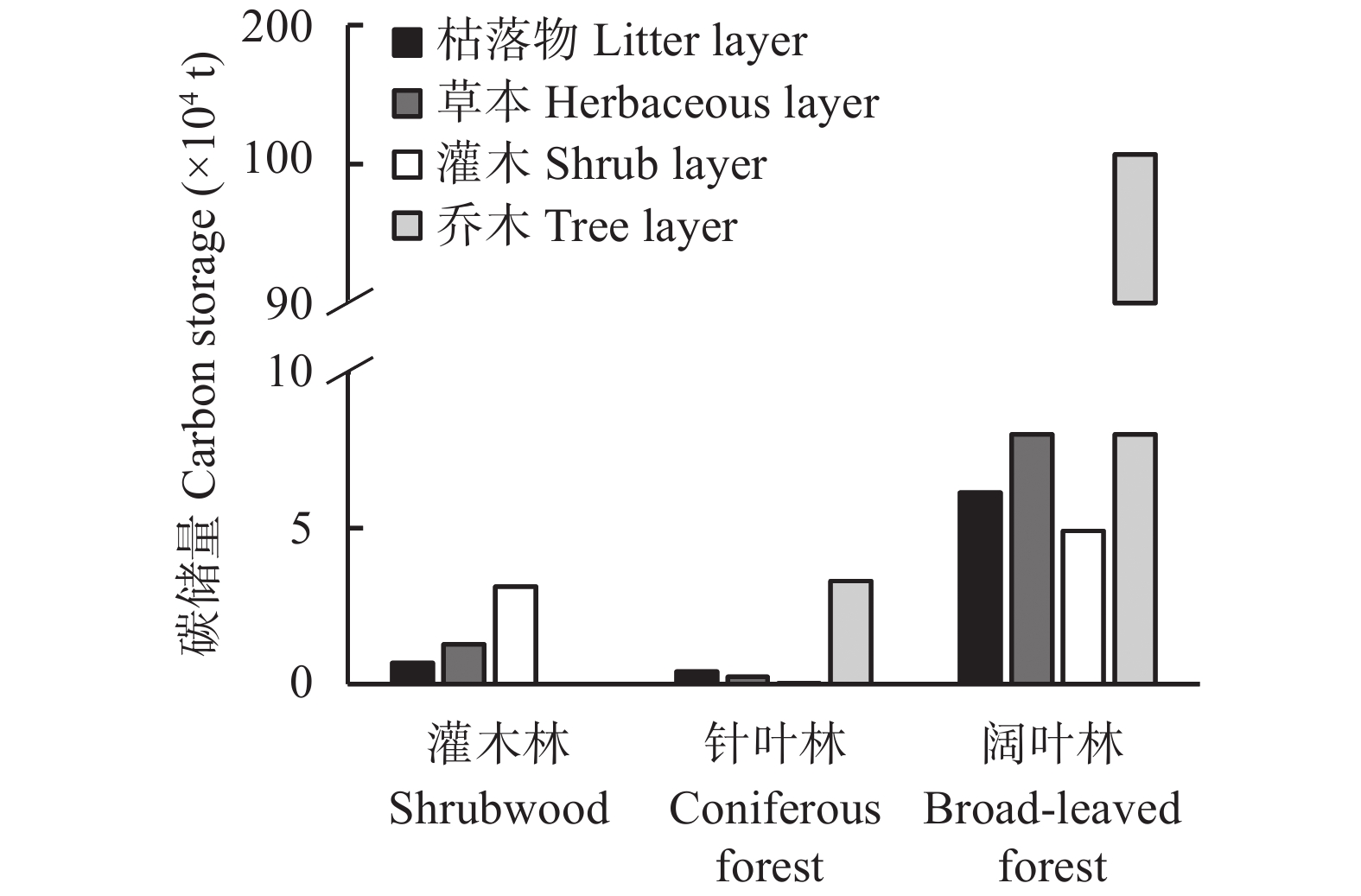
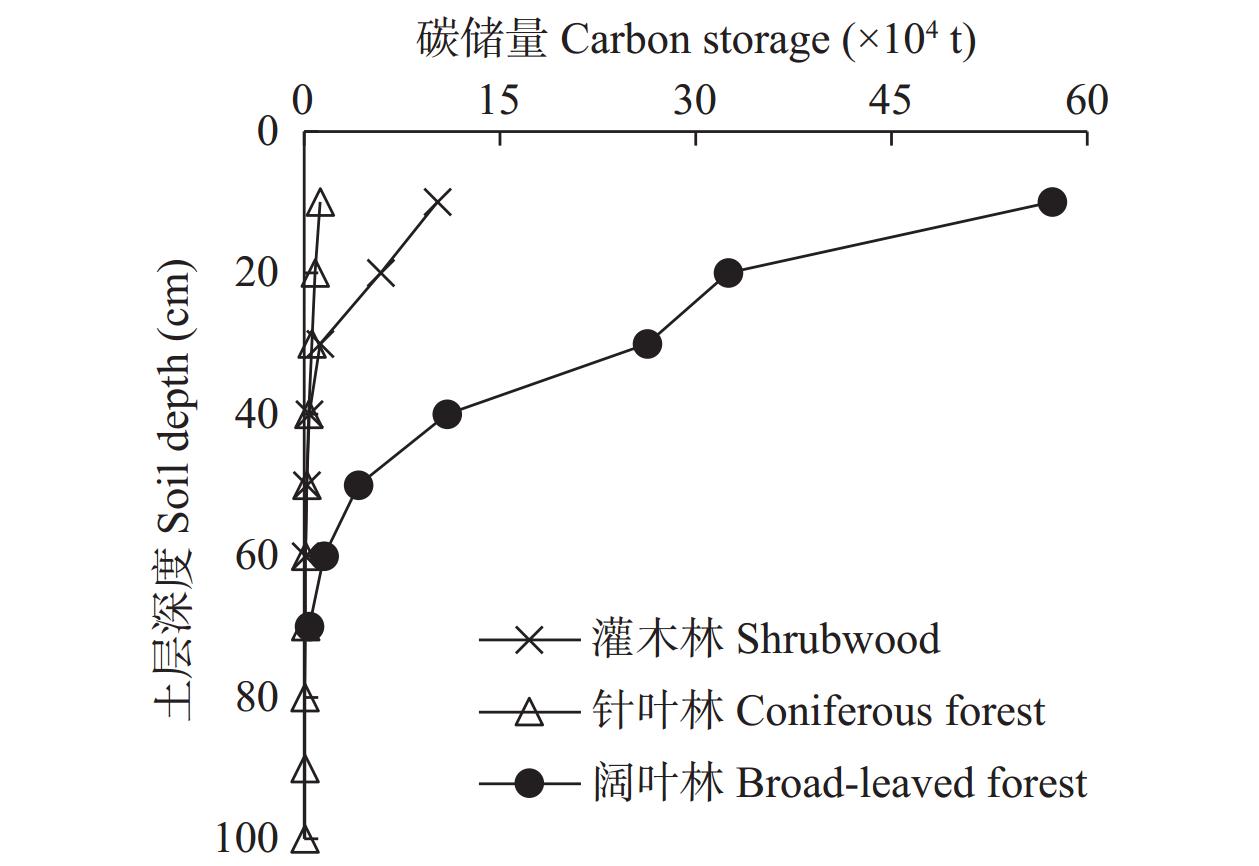
森林生态系统是陆地生态系统的主要碳库, 准确评估其碳储量, 探明其分布特征对区域碳汇管理及生态修复具有重要意义。本文以太行山区典型流域—柳林河流域的森林生态系统为研究对象, 基于样地清查法, 对区域内森林生态系统碳密度和碳储量分布特征展开研究。结果表明: 1) 柳林河流域森林生态系统碳密度为20.80 kg·m−2, 碳储量为2.95×106 t(C); 2)在空间上, 随海拔升高森林生态系统碳密度由15.12 kg·m−2持续增加到27.34 kg·m−2, 碳储量呈先增大后降低的变化趋势, 并于700~900 m海拔处达最大, 阴坡平均碳密度和碳储量均高于阳坡; 3)在垂直组成上, 灌木林与阔叶林中土壤层(0~100 cm)碳储量分别占森林总碳储量的77.87%和51.41%, 而在针叶林中植被层碳储量占主导地位, 占比为53.89%, 各林型中土壤层碳密度和碳储量均随土壤深度的增加而减少, 表层土壤(0~20 cm)碳储量占土壤层(0~100 cm)总碳储量的69.91%。柳林河流域森林生态系统碳密度与全国森林生态系统平均碳密度仍存在一定差距, 未来应继续加强该区域特别是低海拔以及阳坡区域森林的经营管理和表层土壤的保护修复, 以提升森林固碳增汇能力。该研究可为太行山流域碳储量评估、生态修复及多因素分析提供数据和理论支撑。
Abstract:Forest ecosystems constitute the main carbon pools in terrestrial ecosystems. It is of great significance to accurately assess the carbon storage of forest ecosystems and determine their distribution characteristics for regional carbon sink management, the scientific formulation of ecological environment protection and land use policies, the promotion of regional low-carbon sustainable development, and the realization of “carbon neutrality”. In this study, the forest ecosystem of the Liulin River Basin, a typical watershed in the Taihang Mountain region, was used as the research object. Based on the sampled land inventory method, the distribution characteristics of carbon density and storage in the forest ecosystems in the region were studied. The results showed that: 1) The carbon density of the forest ecosystem in the Liulin River Basin was 20.80 kg·m−2, and the carbon storage was 2.95 × 106 t(C). 2) Spatially, the carbon density of forest ecosystems showed an increasing trend with increasing altitude. The carbon density continued to increase from 15.12 kg·m−2 to 27.34 kg·m−2 with altitude. The carbon storage initially showed an increasing trend, thereafter decreasing with an increase in altitude, reaching the maximum at an altitude of 700−900 m. Additionally, the average carbon density and the carbon storage of the shady slope was higher than that of the sunny slope. 3) In terms of vertical composition, the carbon storage in the 0−100 cm soil layer in the shrubwood and broad-leaved forests accounted for 77.87% and 51.41% of the total carbon storage in the forest ecosystem, respectively, whereas carbon storage in the vegetation layer was dominant in the coniferous forest, accounting for 53.89%. In coniferous and broad-leaved forests, the carbon density and carbon storage of the tree layer were higher than those of the other vegetation layers. Carbon density and carbon storage in the soil layer of each forest type decreased with increasing soil depth, and carbon storage in the surface soil (0−20 cm) accounted for 69.91% of the total carbon storage in the 0−100 cm soil layer. A gap remains between the carbon density of forest ecosystems in the Liulin River Basin and the average carbon density of forest ecosystems in China. The management of forest ecosystems and the protection and restoration of surface soil in this region, especially in low-altitude and sunny slope areas, will need to be strengthened to enhance forest carbon sequestration and sink capacity. This study not only provides data and theoretical support for carbon storage assessment, ecological restoration, and multi-factor analysis in the Taihang Mountains, but also provides a data and theoretical basis for the management and afforestation of forest ecosystems and carbon sequestration in the Taihang Mountains and similar regions.
-
-
表 1 太行山典型流域不同海拔阴坡与阳坡碳密度
Table 1 Carbon density of shady slope and sunny slope at different altitudes in typical watersheds of Taihang Mountains Basin
kg·m−2 坡向
Slope aspect海拔 Altitude (m) 总流域 Whole basin 300~500 500~700 700~900 900~1100 1100~1300 阴坡 Shady slope 20.15 19.35 19.27 35.84 37.76 26.47 阳坡 Sunny slope 10.08 19.61 18.29 10.85 16.91 15.15 平均 Mean 15.12 19.48 18.78 23.35 27.34 20.80 表 2 柳林河流域不同海拔阴坡与阳坡碳储量
Table 2 Carbon storage on shady slopes and sunny slopes at different altitudes in the Liulin River Basin
t(C) 坡向
Slope aspect海拔 Altitude (m) 合计 Total 300~500 500~700 700~900 900~1100 1100~1300 阴坡 Shady slope 6.14×104 2.58×105 4.71×105 5.72×105 3.41×105 1.70×106 阳坡 Sunny slope 3.07×104 2.62×105 4.47×105 1.91×105 3.17×105 1.25×106 合计 Total 9.21×104 5.20×105 9.17×105 7.63×105 6.58×105 2.95×106 -
[1] 杨阳, 张萍萍, 吴凡, 等. 黄土高原植被建设及其对碳中和的意义与对策[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(21): 9071−9081 YANG Y, ZHANG P P, WU F, et al. The significance and countermeasures of vegetation construction on the Loess Plateau to carbon neutrality[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(21): 9071−9081
[2] 柴麒敏. 中国新达峰目标与碳中和愿景的政策展望[J]. 世界环境, 2021(1): 20−22 CHAI Q M. Policy outlook on China’s new goal of peaking carbon dioxide emissions and vision of carbon neutrality[J]. World Environment, 2021(1): 20−22
[3] FANG J Y, KATO T, GUO Z D, et al. Evidence for environmentally enhanced forest growth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(26): 9527−9532
[4] GE Y, AVITABILE V, HEUVELINK G B M, et al. Fusion of pan-tropical biomass maps using weighted averaging and regional calibration data[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2014, 31: 13−24 doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2014.02.011
[5] JANZEN H H. Carbon cycling in earth systems — A soil science perspective[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2004, 104(3): 399–417
[6] PAQUETTE A, MESSIER C. The role of plantations in managing the world’s forests in the Anthropocene[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2010, 8(1): 27−34 doi: 10.1890/080116
[7] 刘兆丹, 李斌, 方晰, 等. 湖南省森林植被碳储量、碳密度动态特征[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(21): 6897−6908 LIU Z D, LI B, FANG X, et al. Dynamic characteristics of forest carbon storage and carbon density in the Hunan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(21): 6897−6908
[8] 王效科, 冯宗炜, 欧阳志云. 中国森林生态系统的植物碳储量和碳密度研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(1): 13−16 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.01.003 WANG X K, FENG Z W, OUYANG Z Y. Vegetation carbon storage and density of forest ecosystems in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001, 12(1): 13−16 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.01.003
[9] 杨玉姣, 陈云明, 曹扬. 黄土丘陵区油松人工林生态系统碳密度及其分配[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(8): 2128−2136 YANG Y J, CHEN Y M, CAO Y. Carbon density and distribution of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation ecosystem in Hilly Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(8): 2128−2136
[10] 方精云, 郭兆迪, 朴世龙, 等. 1981—2000年中国陆地植被碳汇的估算[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2007, 37(6): 804−812 FANG J Y, GUO Z D, PIAO S L, et al. Estimation of carbon sinks of terrestrial vegetation in China from 1981 to 2000[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2007, 37(6): 804−812
[11] 徐新良, 曹明奎, 李克让. 中国森林生态系统植被碳储量时空动态变化研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2007, 26(6): 1−10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2007.06.001 XU X L, CAO M K, LI K R. Temporal-spatial dynamics of carbon storage of forest vegetation in China[J]. Progress in Geography, 2007, 26(6): 1−10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2007.06.001
[12] 李海奎, 雷渊才, 曾伟生. 基于森林清查资料的中国森林植被碳储量[J]. 林业科学, 2011, 47(7): 7−12 doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20110702 LI H K, LEI Y C, ZENG W S. Forest carbon storage in China estimated using forestry inventory data[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2011, 47(7): 7−12 doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20110702
[13] 陈碧海, 吴林芳, 何碧胜, 等. 海拔梯度对广东古兜山木本植物生物量及碳储量的影响[J]. 林业与环境科学, 2020, 36(5): 97−103 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4427.2020.05.016 CHEN B H, WU L F, HE B S, et al. Effects of altitude gradient on biomass and carbon storage of woody plants in Gudoushan, Guangdong Province[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science, 2020, 36(5): 97−103 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4427.2020.05.016
[14] 董金相. 戴云山黄山松林碳储量及其影响因子研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2012 DONG J X. Study on the carbon storage of Pinus taiwanensis and the factors of influence of it in Daiyun Mountain[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012
[15] 丛俊霞, 郑晓, 朱教君, 等. 沙地樟子松天然林地上碳储量估算及其空间分布特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(11): 2997−3007 CONG J X, ZHENG X, ZHU J J, et al. Estimation and spatial distribution of aboveground carbon storage for natural Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests on sandy land[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(11): 2997−3007
[16] 黄从德, 张健, 杨万勤, 等. 四川省森林植被碳储量的空间分异特征[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(9): 5115−5121 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.062 HUANG C D, ZHANG J, YANG W Q, et al. Spatial differentiation characteristics of forest vegetation carbon stock in Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(9): 5115−5121 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.062
[17] 王义贵, 徐干君, 白明, 等. 巫山针叶林与阔叶林乔灌草结构特征及碳汇功能对比[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 98−106 WANG Y G, XU G J, BAI M, et al. Comparison of structural characteristics and carbon sink functions between trees, shrubs and herbs of coniferous and broadleaf forests in Wushan[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2023, 43(10): 98−106
[18] 白昆立, 陈蕾伊, 邓洪涛, 等. 华南地区不同类型森林生态系统植被碳现状研究[J]. 林业与环境科学, 2022, 38(6): 102−108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4427.2022.06.016 BAI K L, CHEN L Y, DENG H T, et al. Vegetation carbon status of different types of forest ecosystems in South China[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science, 2022, 38(6): 102−108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4427.2022.06.016
[19] 唐志明, 刘炳响, 屈宇. 河北太行山区典型水土保持林乔木层生物量及碳储量研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(1): 102−107, 135 TANG Z M, LIU B X, QU Y. Study on biomass and carbon storage of Arbor layers in typical soil and water conservation forests in Taihang Mountain range in Hebei Province[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2020(1): 102−107, 135
[20] 王南. 太行山低山丘陵区坡向对荆条灌丛生物量及碳储量的影响[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2020 WANG N. Effect of slope aspect on biomass and carbon storage of Vitex negundo var. heterophylla shrub in low mountains and hilly area of Taihang mountains[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2020
[21] 王成武, 罗俊杰, 唐鸿湖. 基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 215−225 WANG C W, LUO J J, TANG H H. Analysis on the driving force of spatial and temporal differentiation of carbon storage in the Taihang Mountains based on InVEST model[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(2): 215−225
[22] 邹耀进. 海南岛灌丛生态系统有机碳及全氮分布特征研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2017 ZOU Y J. Study on distribution characteristics of organic carbon and total nitrogen in shrub ecosystem of Hainan Island[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2017
[23] 田勇燕, 秦飞, 言华, 等. 我国常见木本植物的含碳率[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(26): 16166−16169 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.26.130 TIAN Y Y, QIN F, YAN H, et al. Carbon content rate in the common woody plants of China[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(26): 16166−16169 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.26.130
[24] 訾园园, 郗敏, 孔范龙, 等. 胶州湾滨海湿地土壤有机碳时空分布及储量[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(7): 2075−2083 ZI Y Y, XI M, KONG F L, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of soil organic carbon and its storage in the coastal wetlands of Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(7): 2075−2083
[25] 尤海舟, 毕君, 王超, 等. 河北小五台山不同海拔白桦林土壤有机碳密度分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(3): 432−437 YOU H Z, BI J, WANG C, et al. Altitudinal distribution rule of Betula platyphylla forest’s soil organic carbon density and its influencing factors in Xiaowutai Mountain in Hebei[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(3): 432−437
[26] 周玉荣, 于振良, 赵士洞. 我国主要森林生态系统碳贮量和碳平衡[J]. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(5): 518−522 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2000.05.002 ZHOU Y R, YU Z L, ZHAO S D. Carbon storage and budget of major Chinese forest types[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2000, 24(5): 518−522 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2000.05.002
[27] 陈璐, 王顺忠, 桑卫国. 我国暖温带森林碳储量特点研究−以北京、河北为例[J]. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 30(2): 34−42 CHEN L, WANG S Z, SANG W G. Characteristics of carbon storage in warm temperate forests in China: A case study of Beijing and Hebei[J]. Journal of Minzu University of China (Natural Sciences Edition), 2021, 30(2): 34−42
[28] 王新闯, 齐光, 于大炮, 等. 吉林省森林生态系统的碳储量、碳密度及其分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(8): 2013−2020 WANG X C, QI G, YU D P, et al. Carbon storage, density, and distribution in forest ecosystems in Jilin Province of Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(8): 2013−2020
[29] 李茂娟, 李天奇, 朱文博, 等. 基于InVEST模型的太行山区生态系统碳储量多维变化研究[J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(6): 631−642, 684 LI M J, LI T Q, ZHU W B, et al. Multidimensional changes of carbon storage in Taihang Mountain ecosystem based on InVEST model[J]. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science), 2021, 51(6): 631−642, 684
[30] 伊锋. 山西太岳山森林碳储量及分布格局研究[D]. 太谷: 山西农业大学, 2017 YI F. Forest carbon reserve and distribution pattern of Taiyue Mountain in Shanxi Province[D]. Taigu: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2017
[31] 高述超, 陈毅青, 陈宗铸, 等. 海南岛森林生态系统碳储量及其空间分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(9): 3558−3570 GAO S C, CHEN Y Q, CHEN Z Z, et al. Carbon storage and its spatial distribution characteristics of forest ecosystems in Hainan Island, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(9): 3558−3570
[32] 林培松, 高全洲. 粤东北山区几种森林土壤有机碳储量及其垂直分配特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2009, 23(5): 243−247 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2009.05.052 LIN P S, GAO Q Z. Study on the soil organic carbon storage and vertical distribution of several forest types in mountain area of Northeast Guangdong[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 23(5): 243−247 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2009.05.052
[33] 高婕. 云浮地区林地土壤有机碳分布特征及碳储量估算[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016 GAO J. Distribution characteristics of soil organic and estimation of carbon stock in the area of Yunfu[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2016
[34] 张立. 松嫩平原南部土壤碳储量及变化特征研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012 ZHANG L. Study on soil carbon storage and variation characteristics of south Songnen Plain[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012
[35] 曹磊, 宋金明, 李学刚, 等. 滨海盐沼湿地有机碳的沉积与埋藏研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(7): 2040−2048 CAO L, SONG J M, LI X G, et al. Deposition and burial of organic carbon in coastal salt marsh: Research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(7): 2040−2048
[36] 周莉, 李保国, 周广胜. 土壤有机碳的主导影响因子及其研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(1): 99−105 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.01.016 ZHOU L, LI B G, ZHOU G S. Advances in controlling factors of soil organic carbon[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2005, 20(1): 99−105 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.01.016
[37] 杨万勤, 邓仁菊, 张健. 森林凋落物分解及其对全球气候变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(12): 2889−2895 YANG W Q, DENG R J, ZHANG J. Forest litter decomposition and its responses to global climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(12): 2889−2895
[38] 刘玥, 杨继松, 于洋, 等. 辽河口不同类型湿地土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(9): 3011−3020 LIU Y, YANG J S, YU Y, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of soil in the Liaohe Estuary wetlands[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(9): 3011−3020
[39] 宋娅丽, 康峰峰, 韩海荣, 等. 自然因子对中国森林土壤碳储量的影响分析[J]. 世界林业研究, 2015, 28(3): 6−12 SONG Y L, KANG F F, HAN H R, et al. Analysis on effect of nature factors on forest soil carbon storage in China[J]. World Forestry Research, 2015, 28(3): 6−12
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 史川,胥辉,张成程. 滇中地区针叶林碳储量遥感反演及动态变化分析. 现代农业研究. 2025(03): 83-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李玉凤,郭飞,莫燕华,秦佳双,马姜明. 两种密度马尾松人工林生态系统碳储量及其分配特征. 广西林业科学. 2024(05): 577-584 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王云霓,李睿瑶,高佳光,福升,桑昊,霍凯宇,边鸿洋. 内蒙古大青山不同林龄华北落叶松人工林乔木层碳密度特征. 内蒙古林业调查设计. 2024(06): 67-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: