A comparison and discussion of observational studies on farmland evapotranspiration in the North China Plain
-
摘要:
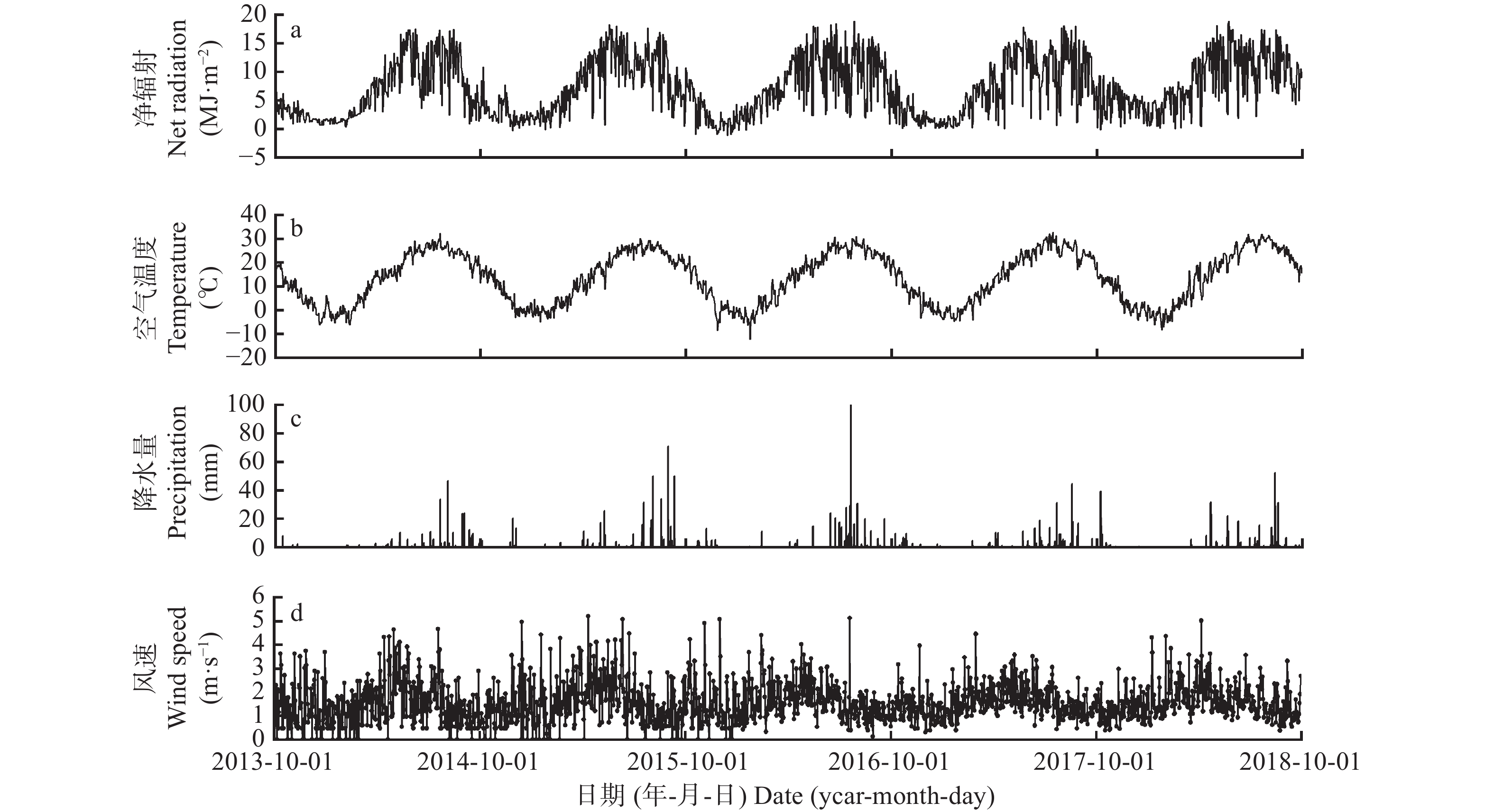
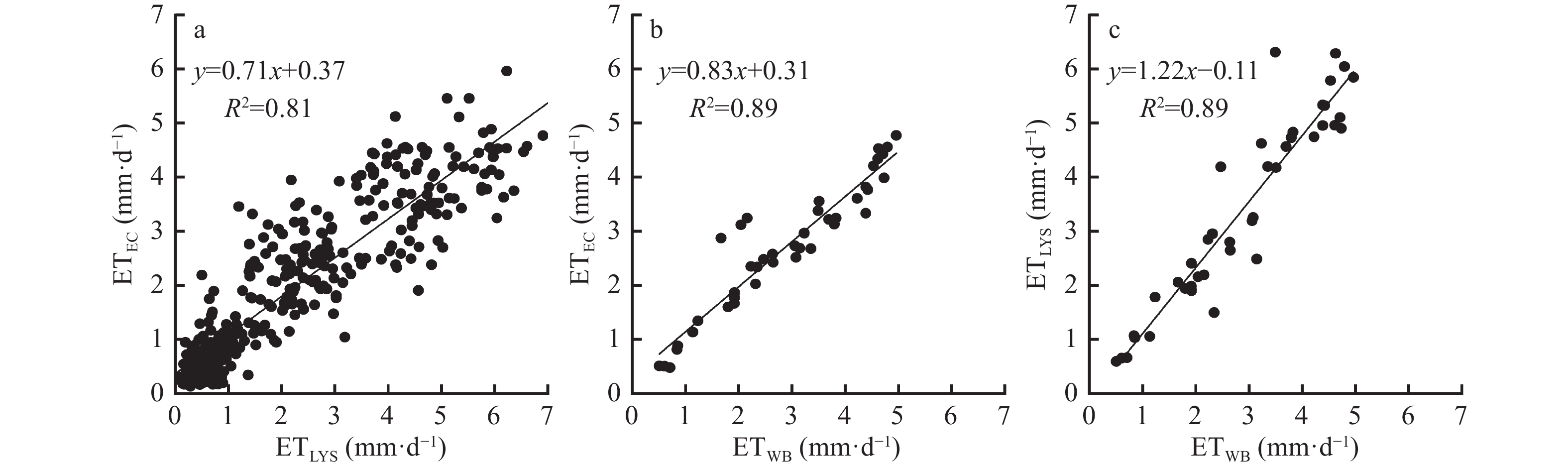
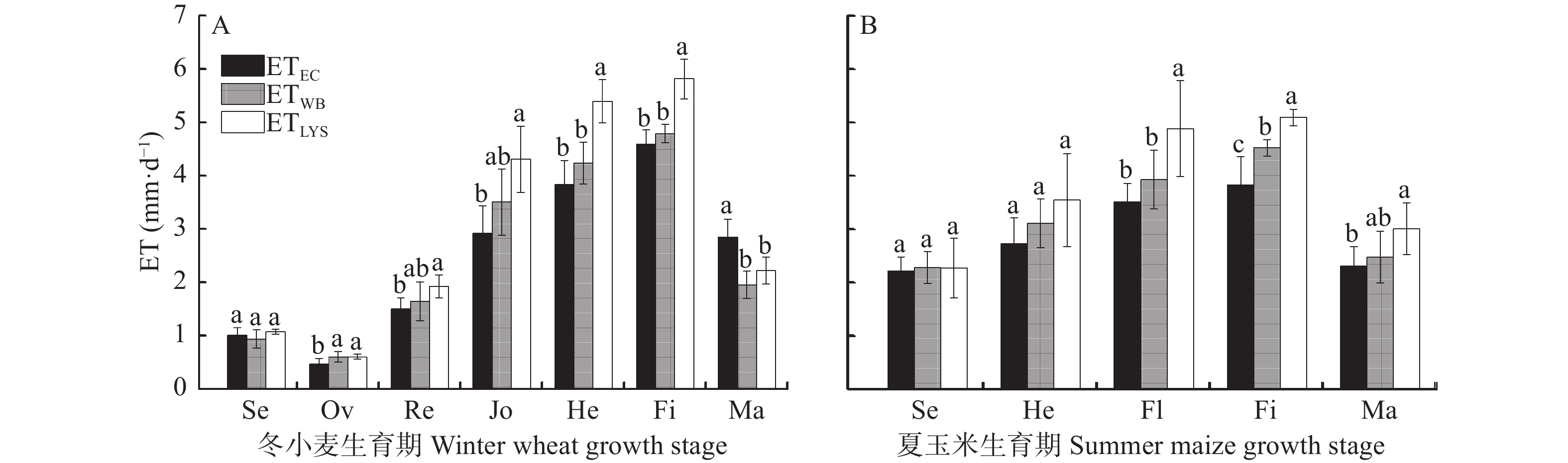
华北平原是我国的粮食主产区之一, 然而该地区水资源非常短缺, 精准测算农田蒸散量(ET)对于该地区合理配置水资源、提高农业用水效率具有非常重要的科学意义和实践价值。本研究利用涡度相关法、水量平衡法和蒸渗仪法对2013年10月—2018年9月的华北平原典型冬小麦-夏玉米一年两熟农田生态系统ET进行了连续的观测对比研究。结果表明: 3种方法测定的ET季节变化趋势基本一致, 且不同方法间ET变化显著正相关, 相关系数r>0.90; 总体表现为蒸渗仪法最高, 水量平衡法和涡度相关法较低, 水量平衡法计算的ET与蒸渗仪法和涡度相关法相关性均为在0.94, 因此其更适于不同尺度ET变化的验证研究。全年来看, 水量平衡法测得的平均年ET为788.6 mm, 比涡度相关法(717.9 mm)高9.8%, 蒸渗仪法测得的年ET为906.4 mm, 比涡度相关法高26.2%。冬小麦关键生育期(拔节期、抽穗期、灌浆期)的ET占生育季总ET的57.3%~61.5%, 夏玉米关键生育期(抽穗期、开花期、灌浆期)的ET占生育季总ET的58.5%~61.6%。综上, 在ET变化及其影响等研究中可以根据研究内容及情况结合各种方法优缺点, 选择适宜的观测方法。
Abstract:The North China Plain is an important grain-producing area in China, and the water resources in this region are limited; therefore, accurately measuring the evapotranspiration (ET) of farmland is of great scientific significance and practical value for the region to reasonably allocate water resources and improve the efficiency of agricultural water use. In this study, ET was measured using the eddy covariance (EC), water balance (WB), and large-scale lysimeter (LYS) methods in a typical winter wheat and summer maize double-cropping agroecosystem in the North China Plain from October 2013 to September 2018. The results showed that the seasonal trends of ET measured by the three methods were generally consistent and were significantly positively correlated among the different methods with a correlation coefficient (r) of more than 0.90; the value of ET measured using the LYS method (ETLYS) was the highest, while the values of the WB method (ETWB) and the EC method (ETEC) were lower. The correlation coefficients between ETWB and ETLYS and ETEC were both approximately 0.94; thus, the WB method was more suitable for validating ET changes at different scales. The average annual ETWB and ETLYS were 788.6 mm and 906.4 mm, which were 9.8% and 26.2% higher than ETEC (717.9 mm), respectively. The ET of winter wheat during the key growth periods (jointing, heading, and filling stages) accounted for 57.3%−61.5% of the total ET during the growing season; for summer maize, the ET in the key growth periods (heading, flowering, and filling stages) accounted for 58.5%−61.6%. In summary, in studies of ET changes and their effects, appropriate observation methods should be selected based on specific objectives and the advantages and disadvantages of the various methods.
-
Keywords:
- Evapotranspiration /
- Eddy covariance /
- Lysimeter /
- Water balance /
- North China Plain
-
-
图 4 涡度相关法(CE)、水量平衡法(WB)和蒸渗仪法(LYS)测得的冬小麦与夏玉米不同生育期的蒸散量(ET)
Se: 幼苗期; Ov: 越冬期; Re: 返青期; Jo: 拔节期; He: 抽穗期; Fl: 开花期; Fi: 灌浆期; Ma: 成熟期。误差线为5年ET的标准差。不同字母表示3种方法在P<0.05水平差异显著。Se: seedling; Ov: overwintering; Re: reviving; Jo: jointing; He: heading; Fl: flowering; Fi: filling; Ma: maturity. The error bars represent the standard deviation of ET for five years. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among three methods (P<0.05).
Figure 4. Evapotranspiration (ET) of winter wheat and summer maize at different growth stages measured by eddy covariance (EC), water balance (WB) and large-scale lysimeter (LYS) methods
表 1 冬小麦和夏玉米生育期划分
Table 1 Division of growth stages (month-day) of winter wheat and summer maize
作物 Crop 生育期 Growth stage 日期(月-日) Date (month-day) 作物 Crop 生育期 Growth stage 日期(月-日) Date (month-day) 冬小麦
Winter wheat幼苗期 Seedling 10-01—10-31 夏玉米
Summer maize幼苗期 Seedling 06-15—07-10 越冬期 Over-wintering 11-01—02-28 抽穗期 Heading 07-11—07-25 返青期 Reviving 03-01—04-01 开花期 Flowering 07-26—08-05 拔节期 Jointing 04-02—04-16 灌浆期 Filling 08-06—08-31 抽穗期 Heading 04-17—05-06 成熟期 Maturity 09-01—09-30 灌浆期 Filling 05-07—05-31 成熟期 Maturity 06-01—06-14 表 2 涡度相关系统所用分析仪相关信息
Table 2 Information about the analyzers used in the eddy covariance system
观测要素 Observed element 仪器 Instrument 高度 Height (m) 三维超声风速 Three-dimensional wind speed CSAT3, Campbell, USA 3.5 CO2/H2O密度 CO2/H2O density Li-7500, Li-COR, USA 3.5 净辐射 Net radiation CNR1, Kipp&Zonen, Netherlands 3.5 降水量 Precipitation HPM155, Campbell, USA 3.5 土壤含水量 Soil water content TDR, CS616, Campbell, USA −2.0 表 3 冬小麦和夏玉米生育季3种方法测定的蒸散对比
Table 3 Comparison of evapotranspiration (ET) measured by three methods during winter wheat and summer maize seasons
作物季节 Crop season 总蒸散 Cumulative ET (mm) 日均蒸散 Daily average ET (mm·d−1) ETEC ETWB ETLYS ETEC ETWB ETLYS 冬小麦 Winter wheat 411.0±18.5c 441.7±10.3b 517.0±14.6a 1.6±0.1c 1.7±0.0b 2.0±0.1a 夏玉米 Summer maize 306.9±17.2c 346.8±15.5b 389.3±30.0a 2.8±0.2c 3.2±0.1b 3.6±0.3a 全年 Whole year 717.9±13.2c 788.6±25.0b 906.4±35.6a 2.0±0.0c 2.2±0.1b 2.5±0.1a EC、WB和LYS分别表示涡度相关法、水量平衡法和蒸渗仪法, 数据为5年平均值±标准差。同行不同字母表示3种方法在P<0.05水平差异显著。EC, WB, and LYS represent the eddy covariance, water balance, and lysimeter methods. The mean and standard deviation for five years are shown. Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences among three methods (P<0.05). -
[1] SUN H Y, ZHANG X Y, LIU X J, et al. Impact of different cropping systems and irrigation schedules on evapotranspiration, grain yield and groundwater level in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 211: 202–209
[2] SUN H Y, SHEN Y J, YU Q, et al. Effect of precipitation change on water balance and WUE of the winter wheat-summer maize rotation in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, 97(8): 1139−1145 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2009.06.004
[3] ZHANG Y C, LEI H M, ZHAO W G, et al. Comparison of the water budget for the typical cropland and pear orchard ecosystems in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 198: 53−64 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2017.12.027
[4] WANG K C, DICKINSON R E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2012, 50(2): RG2005
[5] 王笑影. 农田蒸散实测方法研究进展[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2004, 20(1): 27−30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2004.01.009 WANG X Y. Study of the measuring methods for evapotranspiration in farmland[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 2004, 20(1): 27−30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2004.01.009
[6] BALDOCCHI D, FALGE E, GU L H, et al. FLUXNET: A new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem-scale carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy flux densities[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2001, 82(11): 2415−2434 doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(2001)082<2415:FANTTS>2.3.CO;2
[7] BALDOCCHI D D, LAW B E, ANTHONI P M. On measuring and modeling energy fluxes above the floor of a homogeneous and heterogeneous conifer forest[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2000, 102(2/3): 187−206 doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00098-8
[8] MASSMAN W. A simple method for estimating frequency response corrections for eddy covariance systems[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2000, 104: 185−198 doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00164-7
[9] MASSMAN W J, LEE X. Eddy covariance flux corrections and uncertainties in long-term studies of carbon and energy exchanges[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2002, 113(1/4): 121−144 doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(02)00105-3
[10] LEE X H, BLACK T A, DENHARTOG G, et al. Carbon dioxide exchange and nocturnal processes over a mixed deciduous forest[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1996, 81(1/2): 13−29 doi: 10.1016/0168-1923(95)02310-0
[11] 汪明霞, 陈晓飞, 王铁梁, 等. 腾发量的测定和计算方法研究综述[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2006(12): 9−12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2006.12.003 WANG M X, CHEN X F, WANG T L, et al. Review on the measuring and calculation methodologies of evapotranspiration[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2006(12): 9−12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2006.12.003
[12] CHÁVEZ J L, HOWELL T A, COPELAND K S. Evaluating eddy covariance cotton ET measurements in an advective environment with large weighing lysimeters[J]. Irrigation Science, 2009, 28(1): 35−50 doi: 10.1007/s00271-009-0179-7
[13] 刘钰, 彭致功. 区域蒸散发监测与估算方法研究综述[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2009, 7(2): 256−264 LIU Y, PENG Z G. A review of monitoring and estimating methods for regional evapotranspiration[J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2009, 7(2): 256−264
[14] 刘浩, 孙景生, 段爱旺, 等. 日光温室萝卜棵间土壤蒸发规律试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(1): 176−180 LIU H, SUN J S, DUAN A W, et al. Experiment on soil evaporation of radish in sunlight greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(1): 176−180
[15] 吕陆鹏, 李润杰. 三江源班玛县高寒草甸植物腾发量测定方法探讨[J]. 青海农林科技, 2020(3): 62−66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9967.2020.03.015 LYU L P, LI R J. Discussion on the determination method of plant evapotranspiration in alpine meadow of Banma County[J]. Science and Technology of Qinghai Agriculture and Forestry, 2020(3): 62−66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9967.2020.03.015
[16] 戚培同, 古松, 唐艳鸿, 等. 三种方法测定高寒草甸生态系统蒸散比较[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(1): 202−211 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.01.023 QI P T, GU S, TANG Y H, et al. Comparison of three methods for measurement of evapotranspiration in an alpine meadow[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(1): 202−211 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.01.023
[17] ZHAO W Z, LIU B, ZHANG Z H. Water requirements of maize in the middle Heihe River basin, China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, 97(2): 215−223 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2009.09.011
[18] 杨光超, 朱忠礼, 谭磊, 等. 怀来地区蒸渗仪测定玉米田蒸散发分析[J]. 高原气象, 2015, 34(4): 1095−1106 doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2014.00114 YANG G C, ZHU Z L, TAN L, et al. Analysis on evapotranspiration of maize field measured by lysimeters in Huailai[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2015, 34(4): 1095−1106 doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2014.00114
[19] 王韦娜, 张翔, 张立锋, 等. 蒸渗仪法和涡度相关法测定蒸散的比较[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(11): 3551−3559 WANG W N, ZHANG X, ZHANG L F, et al. A comparison study of the evapotranspiration measured by lysimeter and eddy covariance[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(11): 3551−3559
[20] WILSON K B, HANSON P J, MULHOLLAND P J, et al. A comparison of methods for determining forest evapotranspiration and its components: sap-flow, soil water budget, eddy covariance and catchment water balance[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2001, 106(2): 153−168 doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00199-4
[21] 杨建房. 西北旱区制种玉米耗水监测与计算方法研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012 YANG J F. Study on monitoring and calculation method of water consumption of seed maize in arid region of Northwest China[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2012
[22] FANG Q X, MA L, GREEN T R, et al. Water resources and water use efficiency in the North China Plain: current status and agronomic management options[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, 97(8): 1102−1116 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2010.01.008
[23] 董宝娣, 刘孟雨, 乔匀周, 等. 不同畦长灌溉对冬小麦产量及水分利用特性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(8): 1080−1087 DONG B D, LIU M Y, QIAO Y Z, et al. Effects of irrigated field border length on grain yield and water use characteristics of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(8): 1080−1087
[24] 张传伟. 华北平原典型灌溉农田水碳通量及水分利用效率研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020 ZHANG C W. Evaluating water/carbon fluxes and water use efficiency of an typical irrigated cropland in North China Plain[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020
[25] 于贵瑞, 孙晓敏, 温学发, 等. 陆地生态系统通量观测的原理与方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006 YU G R, SUN X M, WEN X F, et al. Principles of Flux Measurement in Terrestrial Ecosystems[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006
[26] 张玉翠, 姜寒冰, 张传伟, 等. 2007—2013年华北平原典型灌溉农田生态系统日通量数据集——以栾城站为例[J]. 中国科学数据, 2020, 5(2): 40–50 ZHANG Y C, JIANG H B, ZHANG C W, et al. Daily fluxes dataset of the typical irrigated agro-ecosystem in the North China Plain: A case study of Luancheng Station (2007–2013)[J]. China Scientific Data, 2020, 5(2): 40–50
[27] BALDOCCHI D D. Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: past, present and future[J]. Global Change Biology, 2003, 9(4): 479−492 doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00629.x
[28] FALGE E, BALDOCCHI D, OLSON R, et al. Gap filling strategies for defensible annual sums of net ecosystem exchange[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2001, 107(1): 43−69 doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00225-2
[29] 屈艳萍, 康绍忠, 张晓涛, 等. 植物蒸发蒸腾量测定方法述评[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2006, (3): 72−77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2009.04.051 QU Y P, KANG S Z, ZHANG X T, et al. A review of methods for measurement of evapotranspiration from plants[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2006, (3): 72−77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2009.04.051
[30] ZHANG X Y, CHEN S Y, SUN H Y, et al. Dry matter, harvest index, grain yield and water use efficiency as affected by water supply in winter wheat[J]. Irrigation Science, 2008, 27(1): 1−10 doi: 10.1007/s00271-008-0131-2
[31] SUN H Y, LIU C M, ZHANG X Y, et al. Effects of irrigation on water balance, yield and WUE of winter wheat in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2006, 85(1/2): 211−218 doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2006.04.008
[32] GU J J, SMITH E A, MERRITT J D. Testing energy balance closure with GOES-retrieved net radiation and in situ measured eddy correlation fluxes in BOREAS[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research–Atmospheres, 1999, 104(D22): 27881−27893 doi: 10.1029/1999JD900390
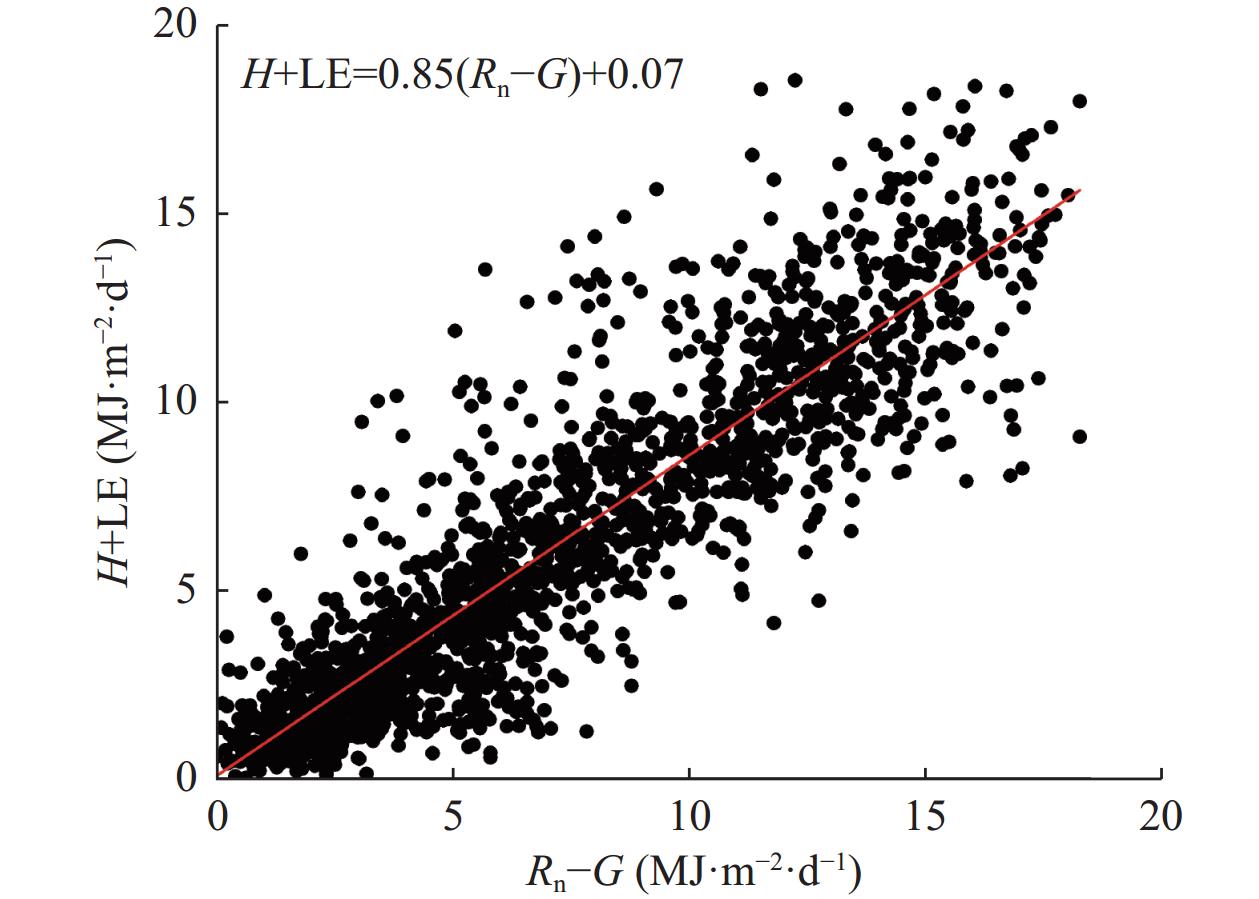
[33] WILSON K, GOLDSTEIN A, FALGE E, et al. Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2002, 113(1/4): 223−243
[34] 杨宾, 左洪超, 董龙翔, 等. 干旱区荒漠下垫面能量通量观测误差对能量闭合的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(2): 451−460 YANG B, ZUO H C, DONG L X, et al. Impact of observation error of desert underlying surface energy flux on energy closure in arid area[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2018, 35(2): 451−460
[35] LEE X H, HU X Z. Forest-air fluxes of carbon, water and energy over non-flat terrain[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2002, 103(2): 277−301 doi: 10.1023/A:1014508928693
[36] 田志伟, 王维真, 王介民. 植被大气间能量储存分项对能量闭合率的影响分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2016, 38(3): 794−803 TIAN Z W, WANG W Z, WANG J M. Analyzing the effects of energy storage terms in vegetation-atmosphere system on energy balance closure[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2016, 38(3): 794−803
[37] XU Z W, MA Y F, LIU S M, et al. Assessment of the energy balance closure under advective conditions and its impact using remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2017, 56(1): 127−140 doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-16-0096.1
[38] LI S E, KANG S Z, ZHANG L, et al. A comparison of three methods for determining vineyard evapotranspiration in the arid desert regions of Northwest China[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2008, 22(23): 4554−4564 doi: 10.1002/hyp.7059
[39] 刘国水, 刘钰, 蔡甲冰, 等. 农田不同尺度蒸散量的尺度效应与气象因子的关系[J]. 水利学报, 2011, 42(3): 284−289 LIU G S, LIU Y, CAI J B, et al. Study on scale effect of farmland evapotranspiration and relationship with meteorological factors[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2011, 42(3): 284−289
[40] ZHANG Y Q, LIU C M, YU Q. Water and heat transfer mechanics in the Soil-Plant-Atmosphere continuum and regional Evapotranspiration model[J]. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2004(4): 562−567



 下载:
下载: