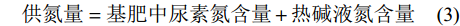Effects of flushing alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid to promote Brassica chinensis yield and nitrogen invertase activity mechanistic research
-
摘要: 污泥通过碱性热水解工艺(ATH)提取的富含多肽、蛋白质类液体(污泥热碱液)已被证实无毒性且可运用于农业生产中, 并显著促进作物生长。为探究污泥热碱液对小青菜氮素吸收及氮代谢调控机制的影响, 本试验以小青菜为研究对象, 采用盆栽试验, 以不施氮肥为对照, 研究5个污泥热碱液处理土壤中分别施入0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1、80.76 mg·kg−1污泥热碱液, 探讨小青菜植株氮素吸收、氮代谢关键酶活性等的变化。结果表明, 随着施用量的增加, 各指标均呈先升高后下降的趋势, 当施用量为40.38 mg·kg−1时, 小青菜收获后氮素累积量、产量和品质等达较高水平, 硝酸盐含量最低。通过对小青菜氮素吸收量及产量进行拟合, 得出121.48~127.59 kg·hm−2为该污泥热碱液对小青菜的最佳施用量。施用量为40.38 mg·kg−1时, 小青菜中硝酸还原酶(NR)、亚硝酸还原酶(NiR)、谷氨酸脱氢酶(GDH)、谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)、谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)均保持较高的活性, 在小青菜定苗后第2周、第4周和第6周与其他处理相比, NR活性增加56.56%~183.43%、16.55%~150.36%和7.86%~293.25%, NiR活性增加24.70%~348.17%、1.06%~71.24%和7.62%~286.59%, GDH活性增加9.91%~149.21%、37.52%~308.35%和16.08%~123.12%, GS活性增加4.13%~17.82%、5.23%~122.27%和9.91%~121.21%, GOGAT活性增加31.31%~288.16%、9.63%~351.69%和28.45%~1274.32%。冗余分析表明小青菜中GOGAT是决定产量、氮素利用率、氮素吸收率的主要因素, 与产量呈显著正相关。施用适量的污泥热碱液会提高小青菜氮素相关转化酶活性, 促进对氮素吸收及产量的增加。热碱液可作为新型肥料施用, 不仅可以解决污泥资源化问题, 还可以提高小青菜产量及养分吸收。Abstract: The polypeptide-rich liquid extracted from alkaline thermal hydrolysis (ATH) sludge has proven to be non-toxic and usable in agricultural production, resulting in a significant increase in crop growth. To explore the effect of ATH hydrolysate on nitrogen uptake and nitrogen metabolism regulation mechanism of Brassica chinensis, B. chinensis was flushed with ATH hydrolysate (0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1, and 80.76 mg·kg−1) treatments, with no nitrogen fertilizer as the control in a pot experiment. The results showed that as the application rate of flushed ATH hydrolysate increased, all indices first increased and then decreased. When the ATH hydrolysate was flushed at 40.38 mg·kg−1, the nitrogen accumulation, yield, and quality of B. chinensis were higher than those of the control after harvest, and the nitrate content was the lowest. By fitting the nitrogen uptake and yield of B. chinensis, the optimal application amount of ATH hydrolysate was determined to be 121.48−127.59 kg·hm−2. Under the condition of 40.38 mg·kg−1 for potted B. chinensis, nitrate reductase (NR), nitrite reductase (NiR), glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), glutamate synthase (GOGAT), and glutamine synthetase (GS) activities could maintain high activity. In the 2nd, 4th, and 6th weeks after final singling of seedlings, the NR activity increased by 56.56%−183.43%, 16.55%−150.36% and 7.86%−293.25%, NiR activity increased by 24.70%−348.17%, 1.06%−71.24% and 7.62%−286.59%, GDH activity increased by 9.91%−149.21%, 37.52%−308.35% and 16.08%−123.12%, GS activity increased by 4.13%−17.82%, 5.23%−122.27% and 9.91%−121.21%, and GOGAT activity increased by 31.31%−288.16%, 9.63%−351.69% and 28.45%−1274.32%. Redundancy analysis showed that GOGAT in B. chinensis was the main factor determining the yield, nitrogen utilization rate, and nitrogen absorption rate, with a significant positive correlation. The ATH hydrolysate solution had a significant influence on the yield of B. chinensis and the activities of enzymes related to nitrogen absorption and transformation under different flushing rates. An appropriate amount of ATH hydrolysate increases the activity of nitrogen-related invertase in B. chinensis, thereby improving the absorption and utilization of nitrogen and yield. At the same time, it also showed that ATH solution can be used as a new type of fertilizer, which not only solves the problem of sludge but also improves the yield and nutrient absorption of B. chinensis.
-
随着城市人口的迅速增加, 生活污泥的排放量日益增多。根据欧盟统计局的数据, 农业利用是欧盟国家最普遍的污泥处置方式之一, 高于我国17.95%~28.71%[1]。在美国, 约有50%左右的污泥通过好氧发酵、厌氧消化等多种方式进行处理, 最终变成肥料进行资源化利用[2]。然而, 我国生活污泥处理主要集中在工业方面, 如厌氧消化产生沼气、低温热解生产燃油、气化生产可燃气体, 但该处理方法易产生有毒物质[3]。目前, 为了资源回收和持续发展, 可从污泥中提取含氮化合物来促进叶菜类作物对养分的吸收[4-5], 而这些化合物是促进植物生长的关键成分, 通常以蛋白质和蛋白质水解产物(如肽、氨基酸、氨等)存在[6]。而在农业应用实践中, 因污泥含有易腐烂有机物、病原微生物和重金属, 不宜直接施用[7-8]。污泥通过热碱水解生产的一种富含多肽、蛋白质、氨基酸的热碱液, 不仅可以用于提取氨基酸等营养物质, 还可以有效避免施入土壤后造成重金属元素的累积[9], 但其在农业生产中应用还鲜有研究。该热碱液用于农业中, 是否可以促进作物的生长发育还有待进一步的研究。
蔬菜作为生活必需品, 为人体提供所需的氨基酸和维生素等营养元素。氮素是植物体内蛋白质和核酸的主要组成元素, 在作物体内发挥不可替代的作用。为追求高产, 设施菜田化肥过量现象严重, 引起土壤质量退化, 蔬菜品质降低, 硝酸盐含量升高。研究表明, 氨基酸肥料与氮肥配合施用可以有效解决这一问题, 合理的施肥结构可促进叶菜类作物的生长和品质[10-11], 而与化肥相比, 氨基酸肥料可提高蔬菜作物的养分利用效率, 提高产量和品质, 并降低农药成本, 保护环境[12]; 同时氨基酸水溶性肥料中大部分的氮素都是水溶性的, 很容易被植物所吸收利用[13]; 氨基酸是蛋白质合成过程中的基本成分, 同时可影响植株相关代谢过程[14]。小青菜(Brassica chinensis)作为叶菜类植株中的代表性作物, 具有生长快、生长期短、复种指数高等特点, 因此需氮量大[15]。而热碱液中富含丰富的氨基酸、蛋白质、多肽类成分, 其中含有大量的氮素, 但对叶菜类氮素转化相关酶活性影响及氮素养分吸收和品质形成尚不清楚。为此, 探究热碱液对作物氮素吸收、同化和利用及品质形成等影响对污泥的无害化利用与作物高产、农业可持续发展尤为重要。
本研究以小青菜为试材, 采用温室盆栽试验, 设置不同的热碱液施用量处理, 以不施氮肥为对照, 通过对小青菜中氮素循环相关酶活性及品质、产量的测定, 明确热碱液对叶菜类作物中氮的吸收利用机制, 为污泥无害化利用、资源化处理及化肥减施增效、农业可持续发展提供理论依据。
1. 材料和方法
本试验在山西农业大学龙城校区温室(37°46′40″N, 112°34′43″E)中进行, 供试盆栽土壤采集于太原市清徐县专业种植合作社菜园(37°36′14″N, 112°20′44″E), 该地区有5年的蔬菜种植史, 主要以种植小白菜(Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis)为主; 属于温带大陆性气候, 年平均气温为10.2~10.6 ℃, 年均降水量为500 mm左右; 土壤类型为砂质壤土, 基础理化性状为: 全氮0.125 g∙kg−1、有效磷8.56 mg∙kg−1、速效钾136.00 mg∙kg−1、有机质14.85 g∙kg−1、pH 7.85。
供试蔬菜为小青菜, 品种为‘夏多美’(北京农种公司)。氮肥为尿素(含N 46%)、磷肥为过磷酸钙(含P2O5 16%)、钾肥为硫酸钾(含K2O 50%)。本研究委托山西晋联环科科技有限公司通过在pH=13、温度为140 ℃、污泥含水率为91%和时间为3 h的条件下将污泥放入高压反应釜中, 加入一定量的去离子水调节其含水率并搅拌均匀, 用CaO粉末调节pH, 设定反应温度, 进行搅拌, 当釜内温度达到设定温度后开始计时, 之后分离浓缩, 进行热碱液的制备[16], 施用前将其pH调至中性。其中主要成分如表1所示, 且重金属含量远低于国家标准《中华人民共和国国家标准肥料中有毒有害物质的限量要求》(GB 38400—2019)与行业标准《中华人民共和国农业行业标准含氨基酸水溶肥料》(NY 1429—2010)。
表 1 热碱液的理化性质Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid性质 Property 含量 Content 性质 Property 含量 Content 有机碳 Organic carbon (g∙L−1) 153.49±9.37 Mg (mg∙L−1) 25.08±1.19 腐殖酸 Humus (g∙L−1) 8.11±0.08 Fe (mg∙L−1) 54.41±5.0 蛋白质 Protein (g∙L−1) 63.6±1.9 Mn (mg∙L−1) 0.27±0.03 多肽 Polypeptide (g∙L−1) 116.7±12.1 Cu (mg∙L−1) 0.12±0.02 游离氨基酸 Free amino acids (g∙L−1) 54.67±5.21 Zn (mg∙L−1) 1.64±0.13 NH4+-N (g∙L−1) 1.28±0.13 Hg (μg∙L−1) 66.23±5.88 NO3−-N (g∙L−1) 0.19±0.04 As (mg∙L−1) 1.78±0.09 N (g∙L−1) 44.08±0.32 Cd (μg∙L−1) 12.29±3.84 P (g∙L−1) 316.0±18.9 Pb (mg∙L−1) 3.02±0.12 K (g∙L−1) 8.75±0.05 Cr (mg∙L−1) 1.81±0.08 Ca (g∙L−1) 55.3±3.7 pH 10.05±0.08 1.1 试验设计与处理
本试验设6个处理, 分别为施用0 kg∙hm−2、52.5 kg∙hm−2、105 kg∙hm−2、157.5 kg∙hm−2、210 kg∙hm−2的热碱液, 用0~20 cm土层、土壤容重为1.3 g∙cm−3换算对应盆栽热碱液的施用量: 0 mg∙kg−1 (T1)、20.19 mg∙kg−1 (T2)、40.38 mg∙kg−1 (T3)、60.57 mg∙kg−1 (T4)、 80.76 mg∙kg−1 (T5), 以不施氮肥(CK)为对照。每个处理重复9次, 共54盆。
塑料盆规格为内径21.5 cm、高15 cm, 每盆装填供试土壤2.5 kg, 除CK处理不施用氮肥外, 其余各处理施用基肥(N为120 mg·kg−1, P2O5为 100 mg·kg−1, K2O为 150 mg·kg−1), 平衡3 d后灌水, 水分入渗均匀后再播种, 每盆播12粒种子, 待幼苗长出3片真叶后进行间苗, 每盆留苗3株, 每日进行称重后浇水, 使土壤孔隙含水量(WFPS)保持在60%。定苗后每隔7 d追施一次热碱液(用柠檬酸调至中性后施用), CK处理浇等量水, 共6次。
定苗后每隔两周每个处理选择3个重复, 采集每盆地上部植株, 到收获共取样3次。在2021年8月10日播种, 于2021年9月26日采收。试验期间的平均温度为(25±5) ℃, 所有植株在病虫害防治方面的处理方式相同。
1.2 常规指标测定
小青菜每次样品采收后称样品鲜重为产量, 部分样品105 ℃下杀青30 min, 70 ℃下烘干至恒重后称干重为生物量; 粉碎过60目筛(孔径0.25 mm)后, 用Kjeldahl法测定植株全氮含量和品质。剩余样品保存至−80 ℃环境中, 用于酶活性测定。叶片SPAD值的测定采用 SPAD-502仪在收获期上午10:00对小青菜绿叶部分进行测定[17]。
1.3 小青菜品质指标测定
可溶性糖用蒽酮-硫酸比色法测定, 可溶性蛋白用考马斯亮蓝法测定, 维生素C含量用2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法测定, 硝酸盐含量用水杨酸比色法测定[18]。
1.4 氮素吸收转化相关酶活性测定
采用酶联免疫吸附法测定硝酸还原酶(NR)、亚硝酸还原酶(NiR)、谷氨酸脱氢酶(GDH)、谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)、谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)活性。分别称取0.1 g小青菜鲜样样本, 加入1 mL提取液, 冰浴研磨, 离心后提取上清液于96孔UV板中, 加入其余试剂, 在不同吸光度条件下用酶标仪进行测定。NR、GDH、GOGAT、GS试剂盒购买于北京索莱宝生物有限公司, NiR试剂盒购买于上海酶联生物有限公司。详细检测方法参照说明书执行。
1.5 参数计算及数据统计分析
$$ \begin{split} &\qquad 氮素吸收效率({\rm{g}}\cdot {\rm{g}}^{-1}) \;({\rm{NUPE}})=(氮素吸收总量/ \\ &供氮量)\times 100 \text{%}^{[19]} \end{split} $$ (1) $$ \begin{split} &\qquad 氮素利用率(\text{%})\;{\rm{(NUE}})=(氮素吸收量-对照组\\ & 氮素吸收量)/供氮量^{[19]} \end{split} $$ (2) $$ 供氮量=基肥中尿素氮含量+热碱液氮含量 $$ (3) 采用SPSS 23.0软件进行方差分析。在P<0.05水平下, 均值以最小显著性差异法进行检验, 用Excel进行线性加平台拟合, 采用Origin 2018进行作图, 用Correlation Plot进行相关性分析, 用Canoco 5软件进行冗余分析(RDA)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同热碱液施用量对小青菜氮素养分吸收和SPAD、产量的影响
小青菜氮素累积量在整个生育期内呈升高趋势(图1A), 在整个生育期前两周增加速率较后两周明显较高, 其中T3、T4处理在整个生育期内均保持较高水平, 且高于CK处理。
![]() 图 1 不同热碱液施用量对各时期小青菜氮素累积量(A)、干生物量(B)的影响图中竖杠为LSD值, P<0.05。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。The upper vertical bar is the LSD value (P<0.05). CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are treatments of applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.Figure 1. Effects of different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments on nitrogen accumulation (A) and dry biomass (B) of Brassica chinensis in different periods
图 1 不同热碱液施用量对各时期小青菜氮素累积量(A)、干生物量(B)的影响图中竖杠为LSD值, P<0.05。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。The upper vertical bar is the LSD value (P<0.05). CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are treatments of applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.Figure 1. Effects of different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments on nitrogen accumulation (A) and dry biomass (B) of Brassica chinensis in different periods小青菜生物量在整个生育期内呈升高趋势(图1B), 各施用热碱液处理较CK均能明显提高生物量, 且与其他施用热碱液处理相比, T3处理在整个生育期内保持较高水平, 3次采样分别高2.36%~56.63%、7.61%~63.68%和1.26%~69.47%, 并且提高小青菜前期的生长发育速率, 加快作物生长。
随着热碱液施用量的增加, SPAD值呈先升高后稳定的趋势(表2), 且热碱液各处理之间均未达到显著差异。与CK相比, 不同热碱液施用处理小青菜产量、氮素累积量均有所提高(表2), 分别增加26.40%~70.74%和41.72%~88.10%; 随着热碱液施用量的增加呈先升高后降低的趋势, 在T3处理中达最大值。随着热碱液施用量的增加, 氮素吸收率及氮素利用率均呈先增加后降低的趋势(表2), 在T3处理中, 氮素吸收率、氮素利用率达到峰值, 比其他处理分别增加0.72%~32.73%和1.51%~33.45%, 说明当热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时, 热碱液对小青菜氮素的吸收利用具有显著效果。
表 2 不同热碱液施用量处理对小青菜氮素吸收利用的影响Table 2. Effects of different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments on nitrogen absorption, utilization of Brassica chinensis处理
TreatmentSPAD 产量
Yield (g∙plant−1)地上部氮素累积
Aboveground nitrogen accumulation (mg∙plant−1)氮素吸收率
Nitrogen uptake efficiency (g∙g−1)氮素利用率
Nitrogen use efficiency (%)CK 22.37±1.13b 40.53±2.59d 83.59±2.81d — — T1 40.30±0.53a 51.23±1.39c 118.46±2.40c 31.59±0.02b 16.67±0.06a T2 40.07±0.87a 63.38±2.44b 147.15±5.95ab 39.24±0.02a 16.87±0.02a T3 40.83±0.49a 69.20±6.49a 157.23±3.20a 41.93±0.02a 19.55±0.02a T4 39.37±0.24a 68.41±3.92a 156.12±1.02ab 41.63±0.02a 19.26±0.02a T5 40.40±0.23a 63.12±2.18b 138.83±9.68b 37.02±0.03ab 14.65±0.03a 同列不同字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively. 2.2 适宜热碱液施用量分析
根据本研究数据, 进行热碱液施用量分析。对小青菜氮素累积量(Y)和热碱液施用量(X)进行二次项及线性加平台拟合, 小青菜氮素吸收量的二次项拟合方程为Y=−0.0027X 2+0.656X+118.88 (R2=0.997)(图2A), 优于线性加平台拟合(R2=0.789) (图2C), 解析方程得出热碱液施用量为121.48 kg∙hm−2时, 氮素累积量最高, 达158.73 mg∙株−1。当施用量从0 kg∙hm−2增加到121.48 kg∙hm−2时, 氮素累积量也随之增加, 之后随着热碱液施用量的增加, 小青菜氮素累积量逐渐降低。
通过对小青菜产量(Y)和热碱液施用量(X)进行二次项及线性加平台拟合, 小青菜产量的二次项拟合方程为Y=−0.0011X 2+0.2807X +51.379 (R2=0.998) (图2B), 优于线性加平台拟合(R2=0.894) (图2D), 解析方程得出热碱液施用量为127.59 kg∙hm−2时, 小青菜产量最高, 达69.29 g∙株−1。当热碱液施用量从0 kg∙hm−2增加到127.59 kg∙hm−2时, 产量也随之增加, 之后随着施用量的增加, 小青菜产量逐渐降低。说明适宜的热碱液施用量可以提高小青菜产量, 当施用量超过一定阈值后, 反而会导致产量的降低, 符合报酬递减规律。
2.3 不同热碱液施用量对小青菜品质的影响
小青菜品质相关的各项指标, 随着热碱液施用量的升高均呈先升高后下降的趋势(硝酸盐除外)。可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖和维生素C含量的最高值均在T3处理, 分别为10.48 mg·g−1、8.08 mg·g−1和45.90 mg·kg−1 (表3)。其中, T3处理可溶性蛋白含量较CK、T1处理分别增加61.73%和31.16%, 差异达显著水平(P<0.05); 可溶性糖含量较CK、T5处理分别显著增加74.14%、55.38% (P<0.05); 维生素C含量较CK、T1和T2分别增加38.34%、27.36%和24.66%, 差异均达显著水平(P<0.05)。
表 3 不同热碱液施用量处理对小青菜品质的影响Table 3. Effects of different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments on quality of Brassica chinensis处理
Treatment可溶性糖
Soluble sugar content (mg·g−1)可溶性蛋白
Soluble protein content (mg·g−1)维生素C
Vitamin C content (mg·kg−1)硝酸盐
Nitrate content (mg·kg−1)CK 4.64±0.50c 6.48±0.51c 33.18±1.56c 74.00±5.03d T1 6.70±0.13ab 7.99±0.61b 36.04±2.43c 962.00±46.35a T2 7.42±0.32a 9.18±0.18ab 36.82±1.27bc 822.00±47.03b T3 8.08±0.26a 10.48±0.38a 45.90±0.66a 668.00±28.75c T4 7.11±0.75a 10.19±0.57a 45.61±4.83a 696.25±67.19c T5 5.20±0.61bc 9.02±0.51ab 43.56±1.44ab 976.75±20.48a 同列不同字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively. 随着热碱液施用量的增加, 硝酸盐含量呈先下降后升高趋势, T2-T4处理的硝酸盐含量分别比T1降低14.55%、30.56%、27.62%。当热碱液施用量增加到一定程度时会提高小青菜体内硝酸盐含量, 与不施用热碱液处理无显著差异, 说明适宜施用该热碱液不仅可以提高小青菜品质, 并且可有效降低小青菜硝酸盐含量, 过量施用反而会产生负效果。
2.4 不同热碱液施用量对小青菜硝态氮同化酶活性的影响
小青菜定苗后第2周、第4周和第6周, NR活性随着热碱液施用量的增加呈先升高后下降的趋势(图3A)。不同时期均在T3处理下小青菜NR活性最高, 比其他处理分别增加56.56%~183.43%、16.55%~150.36%和7.86%~293.25%。同时, 在定苗后第2周及第4周随着热碱液施用量的增加, 各处理间差异显著; 在第6周, 随着施用量的增加, NR 活性呈先升高后下降再升高的趋势, T3处理中最高, T4处理最低。生长发育后期较高热碱液施用量下NR活性再次升高, 可能是因为作物生长后期积累过多硝酸盐, 刺激作物使得NR活性增加, 从而降低小青菜植物体内硝酸盐含量[20]。
![]() 图 3 不同热碱液施用量处理对各时期小青菜硝酸还原酶(NR) (A)与亚硝酸还原酶(NiR) (B)活性的影响不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.Figure 3. Nitrate reductase (NR) (A) and nitrite reductase (NiR) (B) activities in Brassica chinensis at different growth stages under different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments
图 3 不同热碱液施用量处理对各时期小青菜硝酸还原酶(NR) (A)与亚硝酸还原酶(NiR) (B)活性的影响不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.Figure 3. Nitrate reductase (NR) (A) and nitrite reductase (NiR) (B) activities in Brassica chinensis at different growth stages under different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments在定苗后第2周、第4周、第6周, 随着热碱液施用量的增加, NiR活性总体呈先升高后下降再升高的趋势(图3B)。第2周和第6周的T3处理中, 小青菜的NiR活性值最大, 分别比其他处理增加24.70%~348.17%和7.62%~286.59%; 在第4周时, T2处理数值最大, 分别比其他处理增加2.59%~75.68%, T3处理与T2处理无显著性差异, 比其他处理增加1.06%~71.24%。说明施用40.38 mg∙kg−1热碱液能够提高亚硝酸还原酶活性, 从而促进对氮素的吸收利用。但在较高热碱液施用量条件下酶活性再次升高, 这可能是由于在较高施肥量下, 因小青菜体内积累过多亚硝酸盐会对其产生毒害作用, 从而提高酶活性, 降低小青菜中亚硝酸盐含量, 保证作物健康地生长发育。
分别在小青菜定苗后第2周、第4周和第6周, GDH 活性随着热碱液施用量的增加呈先升高后降低趋势(图4A)。T3处理小青菜中GDH活性最高, 分别比其他处理增加9.91%~149.21%、37.52%~308.35%和16.08%~123.12%。同时当热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时, 小青菜体内GDH活性随生长发育保持较高水平, 促进作物对谷氨酸的合成, 提高作物对氮素的吸收同化。
![]() 图 4 不同热碱液施用量处理中各时期小青菜中谷氨酸脱氢酶(GDH)(A)、谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)和谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)(B)活性不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.Figure 4. Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH, A), glutamate synthase (GOGAT) and glutamine synthase (GS) (B) activities in Brassica chinensis at different stages under different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid flush treatments
图 4 不同热碱液施用量处理中各时期小青菜中谷氨酸脱氢酶(GDH)(A)、谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)和谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)(B)活性不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.Figure 4. Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH, A), glutamate synthase (GOGAT) and glutamine synthase (GS) (B) activities in Brassica chinensis at different stages under different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid flush treatments在小青菜定苗后第2周, 各处理间GS活性无显著差异。在第4周、第6周, GS活性随着热碱液施用量的增加呈先升高后下降趋势(图4B), 在3个检测时期内均以T3处理最高, 分别比其他处理增加4.13%~17.82%、5.23%~122.27%和9.91%~121.21%, 说明在该时期施用热碱液可提高小青菜中GS活性, 并且在施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时效果最好。
在小青菜定苗后第2周、第4周和第6周, 与GS变化趋势相同, 随着热碱液施用量的增加, GOGAT活性呈先升高后下降趋势(图4B), T3处理小青菜GOGAT活性比其他处理分别增加31.31%~288.16%、9.63%~351.69%和28.45%~1274.32%, 从而促进GS-GOGAT循环, 提高氮素的吸收利用。定苗后小青菜体内GS活性随生长发育呈下降趋势, 热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时可提高小青菜体内GS活性峰值, 促进谷氨酰胺的形成。定苗后小青菜体内GOGAT活性随生长发育呈升高后趋于稳定状态, 在施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1条件下高于其他处理, 并在小青菜整个生育期保持较高水平, 以此保持对氮素较高水平的吸收转化。
总体而言, 在小青菜生长发育期间施用热碱液可明显提高小青菜中GDH、GOGAT、GS活性, 并且在热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时效果最佳, 从而提高小青菜对氮素的吸收利用。
2.5 不同时期小青菜氮素相关酶与产量、氮素吸收利用的相关性及冗余分析
氮素同化相关酶活性与产量、氮素吸收率、氮素利用率的相关性分析如表4所示: 定苗后第2周, 产量和GOGAT呈显著正相关(P<0.05), 氮素吸收率和NR呈显著正相关(P<0.05), 氮素利用率和NR呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。RDA的结果表明, GOGAT和GDH分别解释了产量等变化的28.5%和28.4% (表5); 它们是影响产量、氮素吸收率和利用率的主导因素; GOGAT与产量呈正相关, NR与氮素吸收率呈正相关, 与氮素利用率呈负相关(图5), 与表4结果一致。
表 4 不同时期小青菜氮同化相关酶活性与产量、氮素吸收利用的相关性Table 4. Pearson’s correlation analysis of nitrogen-related enzymes activities and yield, nitrogen absorption and utilization at different periods氮素同化相关酶
Nitrogen assimilation-related enzyme第2周 The second week 第4周 The fourth week 第6周 The sixth week 产量
YieldNUPE NUE 产量
YieldNUPE NUE 产量
YieldNUPE NUE NR 0.331 0.482* −0.514* 0.007 −0.107 −0.241 0.632** 0.746** −0.240 NiR 0.068 0.276 −0.214 0.013 0.142 −0.118 0.340 0.304 −0.051 GDH −0.258 −0.307 0.007 −0.297 −0.202 −0.124 −0.609** −0.674** 0.192 GOGAT 0.542* 0.401 −0.181 0.227 0.493* −0.367 0.354 0.288 −0.161 GS 0.169 0.337 −0.400 −0.354 −0.259 −0.105 −0.463 −0.541* 0.232 *表示显著性为P<0.05, **表示显著性为P<0.01; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶; NUPE: 氮素吸收效率; NUE: 氮素利用率。* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase; NUPE: nitrogen absorption efficiency; NUE: nitrogen use efficiency. 表 5 不同时期氮同化相关的酶活性冗余分析Table 5. Redundancy analysis of enzymes activities related to nitrogen assimilation at different periods氮素同化相关酶
Nitrogen assimilation related enzyme第2周 The second week 第4周 The fourth week 第6周 The sixth week Explains (%) F P Explain (%) F P Explain (%) F P NR 1.7 0.6 0.466 13.8 3.6 0.064 38.8 10.2 0.01 NiR 2.6 0.9 0.366 2.2 0.6 0.454 <0.1 <0.1 0.94 GDH 28.4 9.9 0.014 8.8 1.9 0.162 17.8 6.2 0.022 GOGAT 28.5 6.4 0.014 15.6 3.2 0.092 32.5 41.7 0.002 GS 5.1 1.9 0.198 12.1 2.2 0.16 0.4 0.5 0.604 NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase. ![]() 图 5 不同时期(A: 第2周; B: 第4周; C: 第6周)不同处理下氮素相关酶与产量、氮素吸收率、氮素利用率的冗余分析(RDA)CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Yield: 产量; NUPE: 氮素吸收率; NUE: 氮素利用率; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively. NUPE: nitrogen absorption efficiency; NUE: nitrogen use efficiency; NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase.Figure 5. Redundancy analysis (RDA) of relationship at different periods (A: the second week; B: the fourth week; C: the sixth week) between nitrogen-related enzymes activies to yield, nitrogen uptake, and utilization
图 5 不同时期(A: 第2周; B: 第4周; C: 第6周)不同处理下氮素相关酶与产量、氮素吸收率、氮素利用率的冗余分析(RDA)CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Yield: 产量; NUPE: 氮素吸收率; NUE: 氮素利用率; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively. NUPE: nitrogen absorption efficiency; NUE: nitrogen use efficiency; NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase.Figure 5. Redundancy analysis (RDA) of relationship at different periods (A: the second week; B: the fourth week; C: the sixth week) between nitrogen-related enzymes activies to yield, nitrogen uptake, and utilization第4周, 氮素吸收率和GOGAT呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。RDA的结果表明, GOGAT影响了产量等变化的15.6% (表5), 是影响产量、 氮素吸收率、氮素利用率的主导因素。GOGAT与氮素吸收率呈正相关(图5), 与表4结果一致。
第6周, 产量、氮素吸收率分别和NR、GDH呈极显著相关(P<0.01), 氮素吸收率和GS呈显著相关(P<0.05)。RDA的结果表明, NR、GOGAT和GDH含量分别解释了产量等变化的38.8%、32.5%和17.8% (表5), 表明它们是影响产量、氮素吸收利用的主导因素。NR与产量、氮素吸收率呈正相关; GDH与产量、氮素吸收率呈负相关; GS与氮素吸收率呈负相关(图5), 与表4结果一致。
2.6 不同时期氮素相关酶与品质、氮素累积量的相关性分析
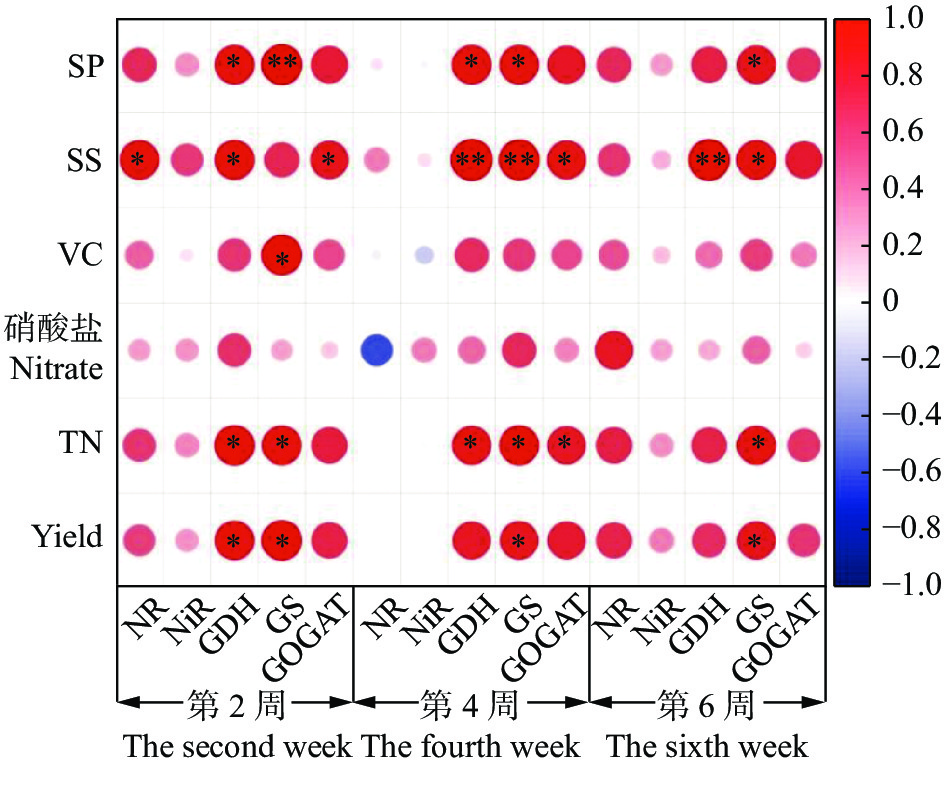
NR在前2周与可溶性糖呈显著正相关(P<0.05), 其余时期并未达显著水平。GDH在前两周与可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖、氮素累积量和产量均呈显著正相关(P<0.05), 在第4周和第6周与可溶性糖呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。GS在整个生育期与可溶性蛋白、氮素累积量和产量呈显著正相关(P<0.05), 其中, 在前两周与可溶性蛋白达极显著正相关(P<0.01), 与维生素C呈显著正相关(P<0.05); 在第4周与可溶性糖呈极显著正相关(P<0.01); 在第6周与可溶性糖呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。GOGAT在第2周与可溶性糖呈显著正相关(P<0.05); 在第4周与可溶性糖和氮素累积量达显著正相关(P<0.05) (图6)。
![]() 图 6 不同时期氮素相关酶与品质、氮素累积量的相关性分析SP: 可溶性蛋白; SS: 可溶性糖; VC: 维生素C; TN: 氮素累积量; Yield: 产量; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。SP: soluble protein; SS: soluble sugar; VC: vitamin C; TN: nitrogen accumulation; NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase. *: P≤0.05; **: P≤0.01.Figure 6. Correlation analysis of nitrogen-related enzymes and quality, nitrogen accumulation at different periods
图 6 不同时期氮素相关酶与品质、氮素累积量的相关性分析SP: 可溶性蛋白; SS: 可溶性糖; VC: 维生素C; TN: 氮素累积量; Yield: 产量; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。SP: soluble protein; SS: soluble sugar; VC: vitamin C; TN: nitrogen accumulation; NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase. *: P≤0.05; **: P≤0.01.Figure 6. Correlation analysis of nitrogen-related enzymes and quality, nitrogen accumulation at different periods3. 讨论
3.1 不同热碱液施用量对小青菜养分吸收及产量的影响
通过实施发展可持续农业来提高作物的养分利用效率和产量是当前全球粮食安全的主要问题之一[21], 采用热碱水解工艺提取的热碱液, 既解决了污泥的处置问题, 同时实现了资源的可持续利用。在此背景下, 我们针对不同施用量的热碱液对小青菜氮素养分吸收、产量等进行了研究。小青菜中氮素累积量随着热碱液施用量的增加呈先升高后降低趋势, 在T3处理最高, 这可能是因为当热碱液氮施用量超过40.38 mg∙kg−1时, 会引起碳氮比过高, 致使微生物的分解较慢, 而且会消耗土壤中的有效态氮素[22], 从而降低了小青菜对氮素的吸收利用, 导致产量降低, 由此说明过量施用热碱液不利于植物养分积累。有研究表明, 油菜(Brassica chinensis)随着施肥量的增加, 地上部养分吸收最初显著增加, 然后保持稳定或显著降低[23]; 同时, 氨基螯合物可显著提高作物的叶片氮浓度[24], 本试验结果与前人研究结果过量施肥量会降低作物养分含量相似。对产量的影响结果表明, 施用热碱液与对照相比能有效提高小青菜产量, 热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时, 产量最高, 超过该施用量后产量呈下降趋势(表2), 这可能是因为该热碱液中含有氨基酸, 作为植物容易获得的生长元素来源, 适量的有机氮有助于蛋白质结构的发育, 热碱液过量后会造成土壤质量下降, 氮素吸收能力下降, 导致产量降低。有研究表明, 氨基酸肥料提供了作物可直接吸收的氮, 比无机氮更易被植物细胞吸收[25], 作物产量又是确定最佳施氮量的常用指标[26]; 有研究发现, 适当污泥施用量比高剂量能够促进叶菜产量的增加[27-29]; 氨基螯合肥对植物生长和产量有显著积极影响[30-32]; 同时, 富含氨基酸的水溶性肥料与持续施用化肥的对照相比, 可显著促进产量的增加[33-34], 热碱液可提高小青菜产量与前人研究结果相似。
3.2 不同热碱液施用量对小青菜品质的影响
本试验通过分析小青菜可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖、维生素C和硝酸盐评价不同施用量的热碱液对小青菜品质的影响(表3), 过低或过高的热碱液施用量会降低小青菜品质含量, 在热碱液施用量为40.38 mg·kg−1时, 上述品质指标均达最高值, 并且此时硝酸盐含量最低(表3), 因此, 适宜的热碱液施用量能够提高小青菜品质。小青菜硝酸盐含量在热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时显著降低, 这很可能是氨基酸与无机态氮共同存在时, 植物偏向于吸收氨基酸, 降低了外源硝态氮的摄入, 同时热碱液施入提高了硝酸还原酶、谷氨酰胺合成酶等氮代谢相关酶的活性, 促进了氮素循环, 从而降低了小青菜中硝酸盐的积累[12]。有研究发现, 小分子氨基酸可提高小青菜品质及降低硝酸盐含量[35]; 也有研究发现, 一定量的酰胺态氮等会提高叶菜类作物的可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖等含量, 并可有效降低其硝酸盐含量[36]。谷氨酸脱氢酶(GDH)可分解谷氨酸为三羧酸循环提供碳骨架, 从而促进糖等物质的合成; 谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)是处于氮代谢中心的多功能酶, 参与多种氮代谢的调节, 其活性的提高可带动氮代谢途径运转, 促进氨基酸的合成和转化[37], 同时, 糖的积累也可促进维生素C的合成[38]。本研究表明, 在小青菜整个生育期GDH与可溶性糖、GS与可溶性蛋白呈显著相关性, 有研究表明, 施用外源含氮物质可提高作物体内GDH、GS和 谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)活性, 从而提高其蛋白质含量[39]。总之, 在热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时, 不仅有利于减少植物中硝酸盐的积累, 而且有利于促进氮转化, 提高作物产量和品质。
3.3 不同热碱液施用量对小青菜氮吸收转化相关酶的影响
氨基酸类肥料施入土壤进入植物体后, 可通过转氨基作用、脱氨基作用及其他过程加以同化, 从而影响植物的氮素循环途径。硝酸还原酶(NR)是植物氮代谢的重要调节和限速酶。NR在植物生长发育、产量形成和蛋白质含量等方面起着重要作用, 在NR的催化作用下, 根系将吸收的NO3-转化为NO2-。在亚硝酸还原酶(NiR)的催化下, NO2-转化为NH4+[40]; NH4+在GDH途径和GS-GOGAT途径中分解和合成氨基酸等。本研究表明, NR及NiR活性随着施用量的增加呈先增加后降低再增加的变化趋势(图3)。这可能是由于在较高施用量下, 植株体内积累过多硝酸盐会对植物产生毒害作用, 从而提高酶活性, 降低小青菜中硝酸盐含量, 同时提供铵态氮同化所需原料, 保证作物的生长发育。在冗余分析中证实了在小青菜生长发育期间, 硝态氮的同化中NR与产量、氮素吸收率之间呈显著相关(图5)。GDH是植物氮素代谢过程中一个关键酶, 能催化谷氨酸的合成和分解[41]。GOGAT具有提高氮素利用效率的作用, GS对氨具有高亲和力, 并直接影响氮的吸收和利用[42]。GS、GOGAT和GDH酶活性的强弱显示了植物将有机氮同化为氨基酸的能力, 其活性受到不同施氮剂量的影响[43]。本研究表明, 小青菜中GDH、GS和GOGAT随着热碱液施用量的增加其活性呈先升高后降低趋势, 在热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时达最大值, 并且在生育关键时期能够保持较高水平(图4), 说明氮的高效利用时期与酶活性时期保持一致, 因此适量的热碱液对作物氮素吸收转化相关酶活性具有良好的促进作用。通过冗余分析表明, 在小青菜生长发育关键时期, 铵态氮的同化中GOGAT与产量、氮素吸收率之间呈显著相关性(图5)。本研究结果同前人关于适量氮肥可提高作物叶片中NR、GS、GOGAT活性, 但过量施用会降低其活性的结果一致[44-45]。同时有研究[46]表明, 添加mM-γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)的营养液在适宜施用量下提高了小白菜中NR、NiR、GS、GOGAT的活性, 与本研究结果一致。综上所述, 氮代谢相关的酶活性的提高是小青菜高产的重要原因之一。氮代谢相关酶活性越高, 氮同化能力越强, 可以合成更多的氨基酸等营养物质, 从而提高产量。
4. 结论
1)通过分别对小青菜产量及氮素吸收量进行拟合分析, 在一定范围内小青菜产量及氮素吸收量随施用量的增加而增加, 当热碱液施用量为127.59 kg∙hm−2时, 小青菜产量达到最高, 当热碱液施用量为121.48 kg·hm−2时, 氮素吸收量达最高, 超过最大限制用量其生长受到抑制。综上所述, 121.48~127.59 kg·hm−2为该热碱液对小青菜的最佳施用量。
2)在热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1的条件下, 小青菜中各品质指标均达到最高值, 此时硝酸盐含量最低, 因此, 适宜的热碱液施用量能提高小青菜品质。
3)不同热碱液施用量对小青菜产量及氮素吸收同化相关酶活性影响较大, 热碱液施用量为40.38 mg∙kg−1时会促进NR、NiR、GDH、GOGAT、GS酶活性提高, 过高或过低的施用量都会不同程度降低其酶活性, 从而影响作物对氮素的吸收同化; 并且在此条件下叶绿素(SPAD值)和产量均达到最高, 其中GOGAT是决定产量、氮素利用率、氮素吸收率的主要因素, 促进了小青菜对氮素的吸收利用。本研究为热碱液对叶菜类作物氮素的作用机理及为热碱液的合理施用提供了依据, 不仅解决了污泥的处置问题, 同时还能提高叶菜类作物的产量。
-
图 1 不同热碱液施用量对各时期小青菜氮素累积量(A)、干生物量(B)的影响
图中竖杠为LSD值, P<0.05。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。The upper vertical bar is the LSD value (P<0.05). CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are treatments of applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.
Figure 1. Effects of different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments on nitrogen accumulation (A) and dry biomass (B) of Brassica chinensis in different periods
图 3 不同热碱液施用量处理对各时期小青菜硝酸还原酶(NR) (A)与亚硝酸还原酶(NiR) (B)活性的影响
不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.
Figure 3. Nitrate reductase (NR) (A) and nitrite reductase (NiR) (B) activities in Brassica chinensis at different growth stages under different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments
图 4 不同热碱液施用量处理中各时期小青菜中谷氨酸脱氢酶(GDH)(A)、谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)和谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)(B)活性
不同小写字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively.
Figure 4. Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH, A), glutamate synthase (GOGAT) and glutamine synthase (GS) (B) activities in Brassica chinensis at different stages under different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid flush treatments
图 5 不同时期(A: 第2周; B: 第4周; C: 第6周)不同处理下氮素相关酶与产量、氮素吸收率、氮素利用率的冗余分析(RDA)
CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Yield: 产量; NUPE: 氮素吸收率; NUE: 氮素利用率; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively. NUPE: nitrogen absorption efficiency; NUE: nitrogen use efficiency; NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase.
Figure 5. Redundancy analysis (RDA) of relationship at different periods (A: the second week; B: the fourth week; C: the sixth week) between nitrogen-related enzymes activies to yield, nitrogen uptake, and utilization
图 6 不同时期氮素相关酶与品质、氮素累积量的相关性分析
SP: 可溶性蛋白; SS: 可溶性糖; VC: 维生素C; TN: 氮素累积量; Yield: 产量; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。SP: soluble protein; SS: soluble sugar; VC: vitamin C; TN: nitrogen accumulation; NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase. *: P≤0.05; **: P≤0.01.
Figure 6. Correlation analysis of nitrogen-related enzymes and quality, nitrogen accumulation at different periods
表 1 热碱液的理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid
性质 Property 含量 Content 性质 Property 含量 Content 有机碳 Organic carbon (g∙L−1) 153.49±9.37 Mg (mg∙L−1) 25.08±1.19 腐殖酸 Humus (g∙L−1) 8.11±0.08 Fe (mg∙L−1) 54.41±5.0 蛋白质 Protein (g∙L−1) 63.6±1.9 Mn (mg∙L−1) 0.27±0.03 多肽 Polypeptide (g∙L−1) 116.7±12.1 Cu (mg∙L−1) 0.12±0.02 游离氨基酸 Free amino acids (g∙L−1) 54.67±5.21 Zn (mg∙L−1) 1.64±0.13 NH4+-N (g∙L−1) 1.28±0.13 Hg (μg∙L−1) 66.23±5.88 NO3−-N (g∙L−1) 0.19±0.04 As (mg∙L−1) 1.78±0.09 N (g∙L−1) 44.08±0.32 Cd (μg∙L−1) 12.29±3.84 P (g∙L−1) 316.0±18.9 Pb (mg∙L−1) 3.02±0.12 K (g∙L−1) 8.75±0.05 Cr (mg∙L−1) 1.81±0.08 Ca (g∙L−1) 55.3±3.7 pH 10.05±0.08 表 2 不同热碱液施用量处理对小青菜氮素吸收利用的影响
Table 2 Effects of different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments on nitrogen absorption, utilization of Brassica chinensis
处理
TreatmentSPAD 产量
Yield (g∙plant−1)地上部氮素累积
Aboveground nitrogen accumulation (mg∙plant−1)氮素吸收率
Nitrogen uptake efficiency (g∙g−1)氮素利用率
Nitrogen use efficiency (%)CK 22.37±1.13b 40.53±2.59d 83.59±2.81d — — T1 40.30±0.53a 51.23±1.39c 118.46±2.40c 31.59±0.02b 16.67±0.06a T2 40.07±0.87a 63.38±2.44b 147.15±5.95ab 39.24±0.02a 16.87±0.02a T3 40.83±0.49a 69.20±6.49a 157.23±3.20a 41.93±0.02a 19.55±0.02a T4 39.37±0.24a 68.41±3.92a 156.12±1.02ab 41.63±0.02a 19.26±0.02a T5 40.40±0.23a 63.12±2.18b 138.83±9.68b 37.02±0.03ab 14.65±0.03a 同列不同字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively. 表 3 不同热碱液施用量处理对小青菜品质的影响
Table 3 Effects of different alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid treatments on quality of Brassica chinensis
处理
Treatment可溶性糖
Soluble sugar content (mg·g−1)可溶性蛋白
Soluble protein content (mg·g−1)维生素C
Vitamin C content (mg·kg−1)硝酸盐
Nitrate content (mg·kg−1)CK 4.64±0.50c 6.48±0.51c 33.18±1.56c 74.00±5.03d T1 6.70±0.13ab 7.99±0.61b 36.04±2.43c 962.00±46.35a T2 7.42±0.32a 9.18±0.18ab 36.82±1.27bc 822.00±47.03b T3 8.08±0.26a 10.48±0.38a 45.90±0.66a 668.00±28.75c T4 7.11±0.75a 10.19±0.57a 45.61±4.83a 696.25±67.19c T5 5.20±0.61bc 9.02±0.51ab 43.56±1.44ab 976.75±20.48a 同列不同字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。CK为不施氮肥对照, T1、T2、T3、T4和T5分别为施氮肥基础上施用热碱液0 mg·kg−1、20.19 mg·kg−1、40.38 mg·kg−1、60.57 mg·kg−1和80.76 mg·kg−1。Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. CK is the control without nitrogen ferilizer. T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 are applicaiton of alkaline thermal hydrolysis liquid of 0 mg·kg−1, 20.19 mg·kg−1, 40.38 mg·kg−1, 60.57 mg·kg−1 and 80.76 mg·kg−1 based on nitrogen application, respectively. 表 4 不同时期小青菜氮同化相关酶活性与产量、氮素吸收利用的相关性
Table 4 Pearson’s correlation analysis of nitrogen-related enzymes activities and yield, nitrogen absorption and utilization at different periods
氮素同化相关酶
Nitrogen assimilation-related enzyme第2周 The second week 第4周 The fourth week 第6周 The sixth week 产量
YieldNUPE NUE 产量
YieldNUPE NUE 产量
YieldNUPE NUE NR 0.331 0.482* −0.514* 0.007 −0.107 −0.241 0.632** 0.746** −0.240 NiR 0.068 0.276 −0.214 0.013 0.142 −0.118 0.340 0.304 −0.051 GDH −0.258 −0.307 0.007 −0.297 −0.202 −0.124 −0.609** −0.674** 0.192 GOGAT 0.542* 0.401 −0.181 0.227 0.493* −0.367 0.354 0.288 −0.161 GS 0.169 0.337 −0.400 −0.354 −0.259 −0.105 −0.463 −0.541* 0.232 *表示显著性为P<0.05, **表示显著性为P<0.01; NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶; NUPE: 氮素吸收效率; NUE: 氮素利用率。* and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively. NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase; NUPE: nitrogen absorption efficiency; NUE: nitrogen use efficiency. 表 5 不同时期氮同化相关的酶活性冗余分析
Table 5 Redundancy analysis of enzymes activities related to nitrogen assimilation at different periods
氮素同化相关酶
Nitrogen assimilation related enzyme第2周 The second week 第4周 The fourth week 第6周 The sixth week Explains (%) F P Explain (%) F P Explain (%) F P NR 1.7 0.6 0.466 13.8 3.6 0.064 38.8 10.2 0.01 NiR 2.6 0.9 0.366 2.2 0.6 0.454 <0.1 <0.1 0.94 GDH 28.4 9.9 0.014 8.8 1.9 0.162 17.8 6.2 0.022 GOGAT 28.5 6.4 0.014 15.6 3.2 0.092 32.5 41.7 0.002 GS 5.1 1.9 0.198 12.1 2.2 0.16 0.4 0.5 0.604 NR: 硝酸还原酶; NiR: 亚硝酸还原酶; GDH: 谷氨酸脱氢酶; GOGAT: 谷氨酸合成酶; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶。NR: nitrate reductase; NiR: nitrite reductase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GOGAT: glutamate synthase; GS: glutamine synthase. -
[1] 单灵婕, 王松林, 孙渝波, 等. 污泥处理处置现状分析与资源化利用研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2020, 38(12): 192−194 SHAN L J, WANG S L, SUN Y B, et al. Analysis of sludge treatment and disposal status and resource utilization[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2020, 38(12): 192−194
[2] WANG L Y. Research progress of resource utilization of sludge[J]. Frontiers in Economics and Management, 2020, 10: 213−215
[3] SOOBHANY N. Insight into the recovery of nutrients from organic solid waste through biochemical conversion processes for fertilizer production: a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 241: 118413 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118413
[4] TANG Y F, DONG B, DAI X H. Hyperthermophilic pretreatment composting to produce high quality sludge compost with superior humification degree and nitrogen retention[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132247 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132247
[5] TEJADA M, GARCÍA-MARTÍNEZ A M, RODRÍGUEZ-MORGADO B, et al. Obtaining biostimulant products for land application from the sewage sludge of small populations[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 50: 31−36 doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.07.006
[6] KELESSIDIS A, STASINAKIS A S. Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries[J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(6): 1186−1195 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.012
[7] YANG G, ZHANG G M, WANG H C. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China[J]. Water Research, 2015, 78: 60−73 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.002
[8] TANG Y F, XIE H, SUN J, et al. Alkaline thermal hydrolysis of sewage sludge to produce high-quality liquid fertilizer rich in nitrogen-containing plant-growth-promoting nutrients and biostimulants[J]. Water Research, 2022, 211: 118036 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.118036
[9] 梁晓红, 刘静, 曹雄. 施氮量对酿造高粱产量和氮素利用率的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2017, 32(17): 179−184 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2017.02.027 LIANG X H, LIU J, CAO X. Effects of nitrogen application rate on yield of brewing sorghum and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2017, 32(17): 179−184 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2017.02.027
[10] CHEN B M, WANG Z H, LI S X, et al. Effects of nitrate supply on plant growth, nitrate accumulation, metabolic nitrate concentration and nitrate reductase activity in three leafy vegetables[J]. Plant Science, 2004, 167(3): 635−643 doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.05.015
[11] WANG J L, LIU Z M, WANG Y, et al. Production of a water-soluble fertilizer containing amino acids by solid-state fermentation of soybean meal and evaluation of its efficacy on the rapeseed growth[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 187: 34−42 doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.07.015
[12] BAKPA E P, XIE J M, ZHANG J, et al. Influence of soil amendment of different concentrations of amino acid water-soluble fertilizer on physiological characteristics, yield and quality of “Hangjiao No. 2” Chili Pepper[J]. PeerJ, 2021, 9: e12472 doi: 10.7717/peerj.12472
[13] SHAFEEK M R, HELMY Y I, SHALABY A M, et al. Response of onion plants to foliar application of sources and levels of some amino acid under sandy soil conditions[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 2012, 8(11): 5521−5527
[14] 袁伟, 董元华, 王辉. 菜园土壤不同施肥模式下小青菜生长和品质及其生态化学计量学特征[J]. 土壤, 2010, 42(6): 987−992 doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2010.06.027 [15] 崔静, 董岸杰, 张卫江, 等. 热碱水解提取污泥蛋白质的实验研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(10): 1889−1892 CUI J, DONG A J, ZHANG W J, et al. Experimental investigation of extracting protein by alkaline thermal sludge hydrolysis from sludge[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009, 3(10): 1889−1892
[16] VERMA K K, ANAS M, CHEN Z L, et al. Silicon supply improves leaf gas exchange, antioxidant defense system and growth in Saccharum officinarum responsive to water limitation[J]. Plants, 2020, 9(8): 1032 doi: 10.3390/plants9081032
[17] 鲍士旦. 土壤农业化学分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000 BAO S D. Agrochemical Analysis of Soil[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000
[18] 罗跃, 张爱华, 王文华, 等. 贵州稻区产量、养分吸收利用对控释尿素的响应[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(5): 81−88 LUO Y, ZHANG A H, WANG W H, et al. Response of yield, nutrient absorption and utilization to controlled-release urea in Guizhou rice region[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(5): 81−88
[19] 宋阳, 崔世茂, 杜金伟, 等. 氮肥不同施用量对葡萄叶片生长及根、叶细胞结构的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2008, 23(3): 204−208 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2008.03.048 SONG Y, CUI S M, DU J W, et al. The grape leaves growth and the anatomical changes both of the grape leaves and roots through different levels of nitrogen fertilizer applications[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2008, 23(3): 204−208 doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2008.03.048
[20] SEARCHINGER T, WAITE R, HANSON C, et al. Creating a sustainable food future: a menu of solutions to feed nearly 10 billion people by 2050. Final report [EB/OL]. (2018−12) [2022–1–15]. https://research.wri.org/wrr-food
[21] TRUONG T H H, MARSCHNER P. Plant growth and nutrient uptake in soil amended with mixes of organic materials differing in C/N ratio and decomposition stage[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2019, 19(3): 512−523 doi: 10.1007/s42729-019-00049-4
[22] DU Y D, SUN J, WANG Z, et al. Effect of ridge film mulching and nitrogen application rate on seed quality, oil yield and nitrogen-use efficiency of winter oilseed rape in Northwest China[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2022, 68(10): 1385−1397 doi: 10.1080/03650340.2021.1894636
[23] SOURI M K, SOORAKI F Y, MOGHADAMYAR M. Growth and quality of cucumber, tomato, and green bean under foliar and soil applications of an aminochelate fertilizer[J]. Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology, 2017, 58(6): 530−536 doi: 10.1007/s13580-017-0349-0
[24] EMAD M H, ABOUKHADRAH S H, SOROUR S G R, et al. Comparison of agronomical and physiological nitrogen use efficiency in three cultivars of wheat as affected by different levels of N sources[C]. Proceeding of 13th International Conference of Agron. Fac. of Agic. Benha: Benha University, 2012: 130–145
[25] WANG H Y, ZHANG Y T, CHEN A Q, et al. An optimal regional nitrogen application threshold for wheat in the North China Plain considering yield and environmental effects[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 207: 52−61 doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2017.03.002
[26] ZHANG H, QI H Y, ZHANG Y L, et al. Effects of sewage sludge pretreatment methods on its use in agricultural applications[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 428: 128213 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128213
[27] GU X B, LI Y N, DU Y D. Optimized nitrogen fertilizer application improves yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of winter rapeseed cultivated under continuous ridges with film mulching[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2017, 109: 233−240 doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.08.036
[28] RATHKE G W, BEHRENS T, DIEPENBROCK W. Integrated nitrogen management strategies to improve seed yield, oil content and nitrogen efficiency of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.): a review[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2006, 117(2/3): 80−108
[29] DATIR R B, APPARAO B J, LAWARES L. Application of amino acid chelated micronutrients for enhancing growth and productivity in chili (Capsicum annum L.)[J]. Plant Sciences Feed, 2012, 2(7): 100−105
[30] ABDELHAMID M T, SHSADAK M, SCHMIDHALTER U. Effect of foliar application of aminoacids on plant yield and physiological parameters in bean plants irrigated with seawater[J]. Acta Biológica Colombiana, 2014, 20(1): 140−152
[31] FAHIMI F, SOURI M K, YAGHOBI F. Growth and development of greenhouse cucumber under foliar application of Biomin and Humifolin fertilizers in comparison to their soil application and NPK[J]. Journal of Science and Technology of Greenhouse Culture, 2016, 7(1): 143−152 doi: 10.18869/acadpub.ejgcst.7.1.143
[32] WANG D S, DENG X H, WANG B, et al. Effects of foliar application of amino acid liquid fertilizers, with or without Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9, on cowpea yield and leaf microbiota[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(9): e0222048 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222048
[33] 张政. 氨基酸态氮对黄瓜的营养效应[D]. 重庆: 西南农业大学, 2005 ZHANG Z. Nutritional effects of amino acid nitrogen on cucumber[D]. Chongqing: Southwest Agricultural University, 2005
[34] 许宗奇, 万传宝, 许仙菊, 等. 肥料增效剂γ-聚谷氨酸对小青菜产量和品质的影响[J]. 生物加工过程, 2012, 10(1): 58−62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2012.01.011 XU Z Q, WAN C B, XU X J, et al. Effects of poly (γ-glutamic acid) application on yield and quality of potted Brassica chinensis[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2012, 10(1): 58−62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2012.01.011
[35] 王丽雪. 氮素形态配比对设施基质栽培韭菜生长、品质及产量的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2021 WANG L X. Effects of nitrogen forms on growth, quality and yield of leek cultivated in protected substrate[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2021
[36] 邱旭华. 水稻氮代谢基础研究: 谷氨酸脱氢酶作用的分子机理[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2009 QIU X H. Basic research on nitrogen metabolism in rice: molecular mechanism of glutamate dehydrogenase[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2009
[37] VEIT-KÖHLER U, KRUMBEIN A, KOSEGARTEN H. Effect of different water supply on plant growth and fruit quality of Lycopersicon esculentum[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 1999, 162(6): 583−588 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2624(199912)162:6<583::AID-JPLN583>3.0.CO;2-P
[38] 夏光利, 董浩, 宋绪鹏, 等. 授高油玉米花粉对普通玉米籽粒蛋白质积累及氮代谢相关酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(7): 13−20 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.07.02 XIA G L, DONG H, SONG X P, et al. Influence of high-oil maize pollen to normal maize kernel protein accumulation and nitrogen metabolism related enzymes activities[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(7): 13−20 doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.07.02
[39] LUO J, QIN J J, HE F F, et al. Net fluxes of ammonium and nitrate in association with H+ fluxes in fine roots of Populus popularis[J]. Planta, 2013, 237(4): 919−931 doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1807-7
[40] DUBOIS F, TERCÉ-LAFORGUE T, GONZALEZ-MORO M B, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase in plants: Is there a new story for an old enzyme?[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2003, 41(6/7): 565−576
[41] KUSANO M, TABUCHI M, FUKUSHIMA A, et al. Metabolomics data reveal a crucial role of cytosolic glutamine synthetase 1;1 in coordinating metabolic balance in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 66(3): 456−466 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04506.x
[42] SHAH J M, BUKHARI S A H, ZENG J B, et al. Nitrogen (N) metabolism related enzyme activities, cell ultrastructure and nutrient contents as affected by N level and barley genotype[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(1): 190−198 doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61308-9
[43] LI D H. Effects of nitrogen application dates on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize in super-high yield conditions[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(4): 852−860
[44] 龙忠富, 刘华荣, 杨义成, 等. 氮肥对不同种植方式百喜草种子产量及其构成因素的影响[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2010, 38(9): 70−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2010.09.022 LONG Z F, LIU H R, YANG Y C, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on seed yield and yield components of Paspalum notatum with different planting patterns[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(9): 70−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2010.09.022
[45] LI J R, TIAN Z, WU X L, et al. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) modulates nitrate concentrations and metabolism in the leaves of pakchoi (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino) treated with a nitrogen-rich solution[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2018, 36(3): 530−542 doi: 10.1007/s11105-018-1092-0
[46] QUAN J, ZHENG W W, WU M F, et al. Glycine betaine and β-aminobutyric acid mitigate the detrimental effects of heat stress on Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) seedlings with improved photosynthetic performance and antioxidant system[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(9): 1213 doi: 10.3390/plants11091213
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 刘佳,曹基武,彭翠英,王靖涵,王旭军. 土壤化学性质对七叶一枝花产量和品质的影响. 中国野生植物资源. 2025(01): 14-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘佳,曹基武,彭翠英,王靖涵,梁军生,廖德志,王旭军. 土壤酚酸类物质对七叶一枝花农艺性状的影响. 湖南林业科技. 2024(02): 10-15+24 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陆奇丰,骆文华. 极小种群广西火桐幼苗对干旱复水的生理响应. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2024(04): 8-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 冯敬华,陈邦清,陈显,曾百林,田风雷,王功芳,余长蓉,曹荣军,张永翠,李道新. 七叶一枝花人工丰产栽培技术研究. 绿色科技. 2024(13): 70-74+78 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘守赞,蒋玲苔,张韵,顾依雯,韩敏琪,李姗,王红珍,白岩. 蓝、紫单色光处理对三叶青生理及总黄酮含量时空变化的影响. 中国生态农业学报(中英文). 2023(06): 885-894 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 周水灯,孙健,江建铭,邵将炜,邓惠敏,邵清松,王志安. 不同生育期施肥对浙贝母产量和品质的影响. 浙江农林大学学报. 2023(04): 756-764 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陆奇丰,骆文华. 不同遮阴环境对广西火桐幼苗生长及生理生化的影响. 西部林业科学. 2023(04): 70-76+82 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 米琪,赵艳丽,李文春,普伟,陆尤,徐萍,于梦雯,陈佳,郑国伟. 云南重楼与球药隔重楼皂苷含量差异及光合特性研究. 时珍国医国药. 2023(12): 2937-2941 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈思,阎凯,何永美,湛方栋,祖艳群,李元,陈建军,李博. 遮阴对伴矿景天Cd、Pb、Zn累积特征的影响. 中国生态农业学报(中英文). 2022(03): 409-418 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 李坤,毛纯,刘军,吴芳兰,杨梅. LED光质对走马胎生长和生理及活性成分含量的影响. 西北植物学报. 2022(05): 819-828 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 许涛,郝心悦,于远航,庄心情,武淑娟,张怡. “药光互补”模式下中草药种植研究概述. 低碳世界. 2022(11): 169-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: